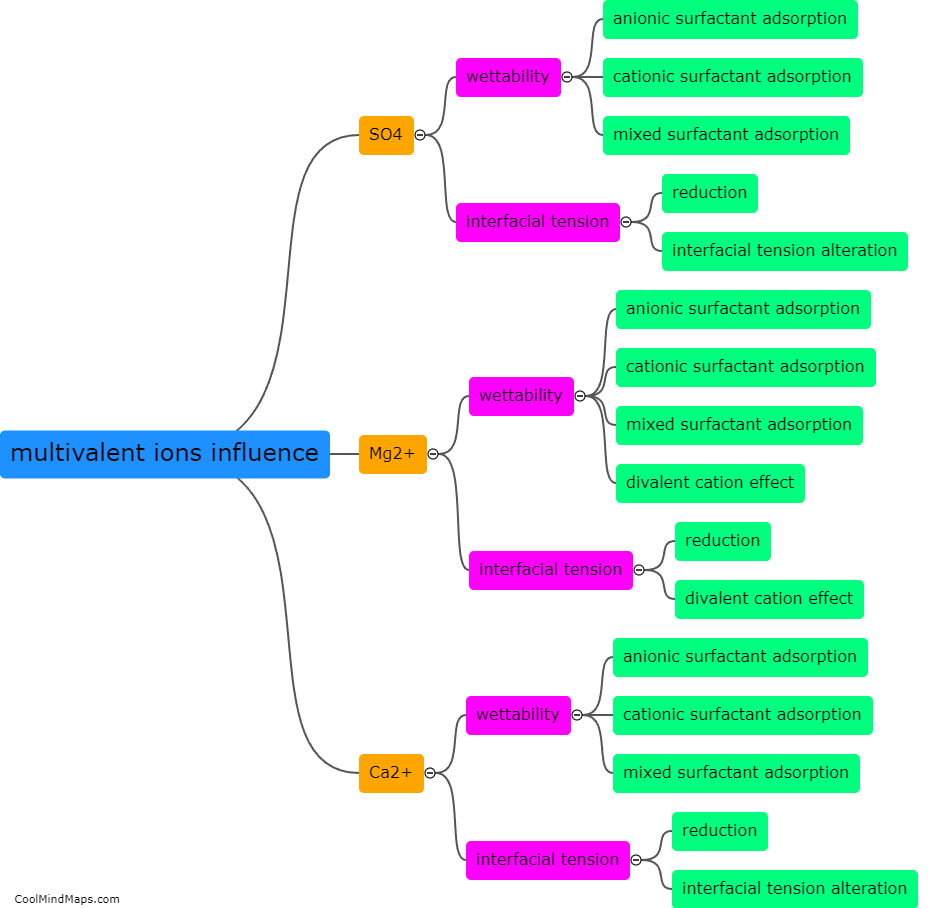
What is the impact of low salinity water flooding on carbonate oil reservoirs?
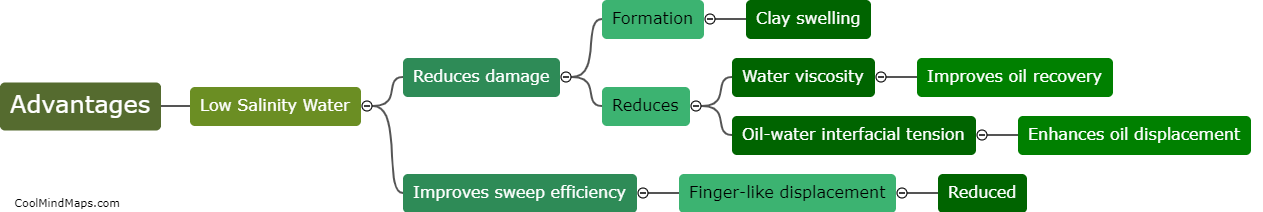
Low salinity water flooding is a method used in the enhanced oil recovery (EOR) process that involves injecting low salinity water into carbonate oil reservoirs. This technique aims to improve oil recovery by altering the chemical interactions at the oil-water-rock interfaces. The impact of low salinity water flooding on carbonate oil reservoirs can be significant. When injected into the reservoirs, the low salinity water interacts with the carbonate rocks, leading to changes in wettability and interfacial tensions, which in turn affect the displacement mechanisms and fluid flow patterns. This alteration can result in improved sweep efficiency, reduction in residual oil saturation, and better recovery rates in carbonate oil reservoirs. However, the impact can vary depending on the specific reservoir characteristics, such as the mineralogy and pore structure, highlighting the need for thorough reservoir characterization and understanding of the underlying mechanisms before implementing low salinity water flooding as an EOR technique.

This mind map was published on 20 December 2023 and has been viewed 85 times.