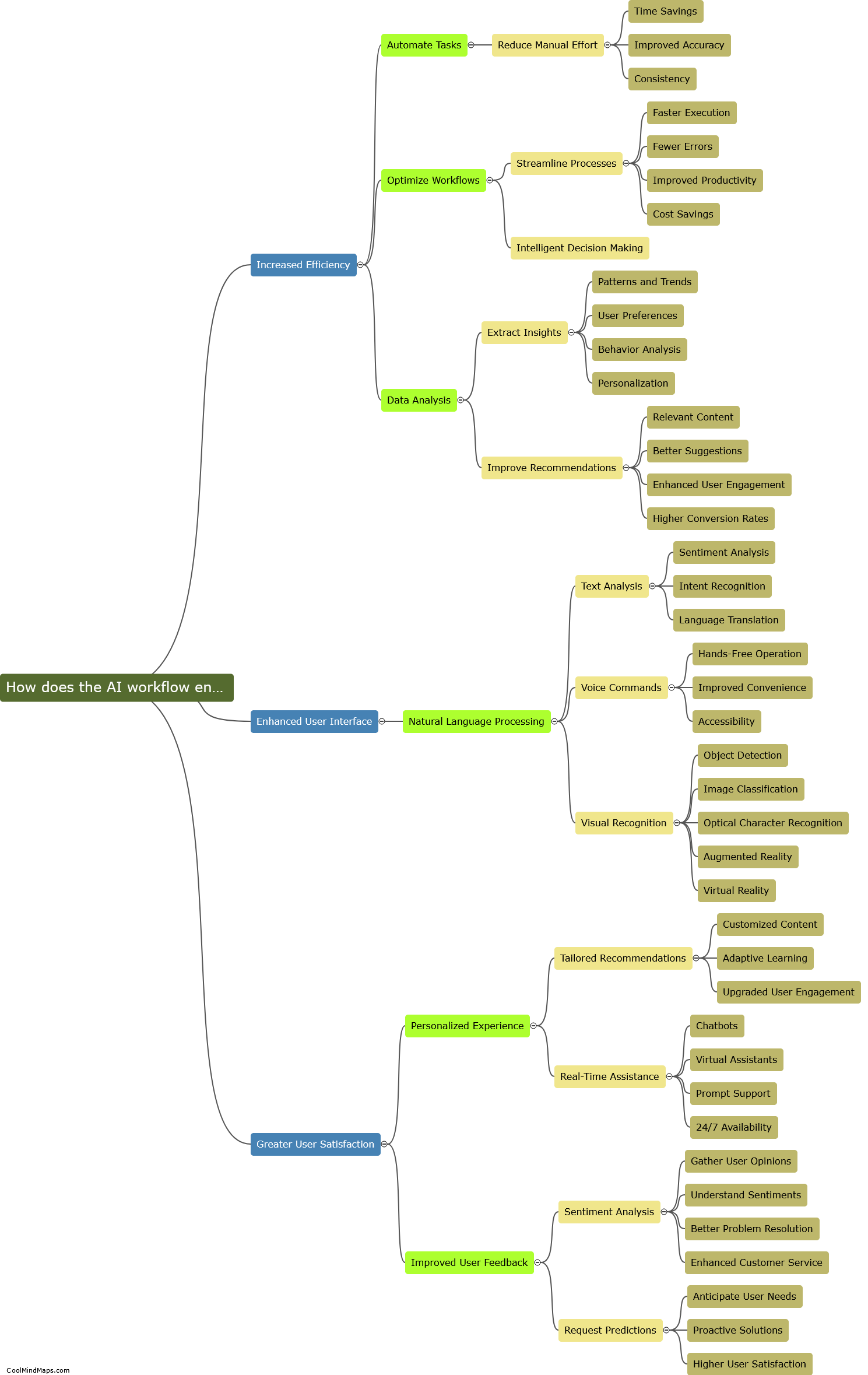
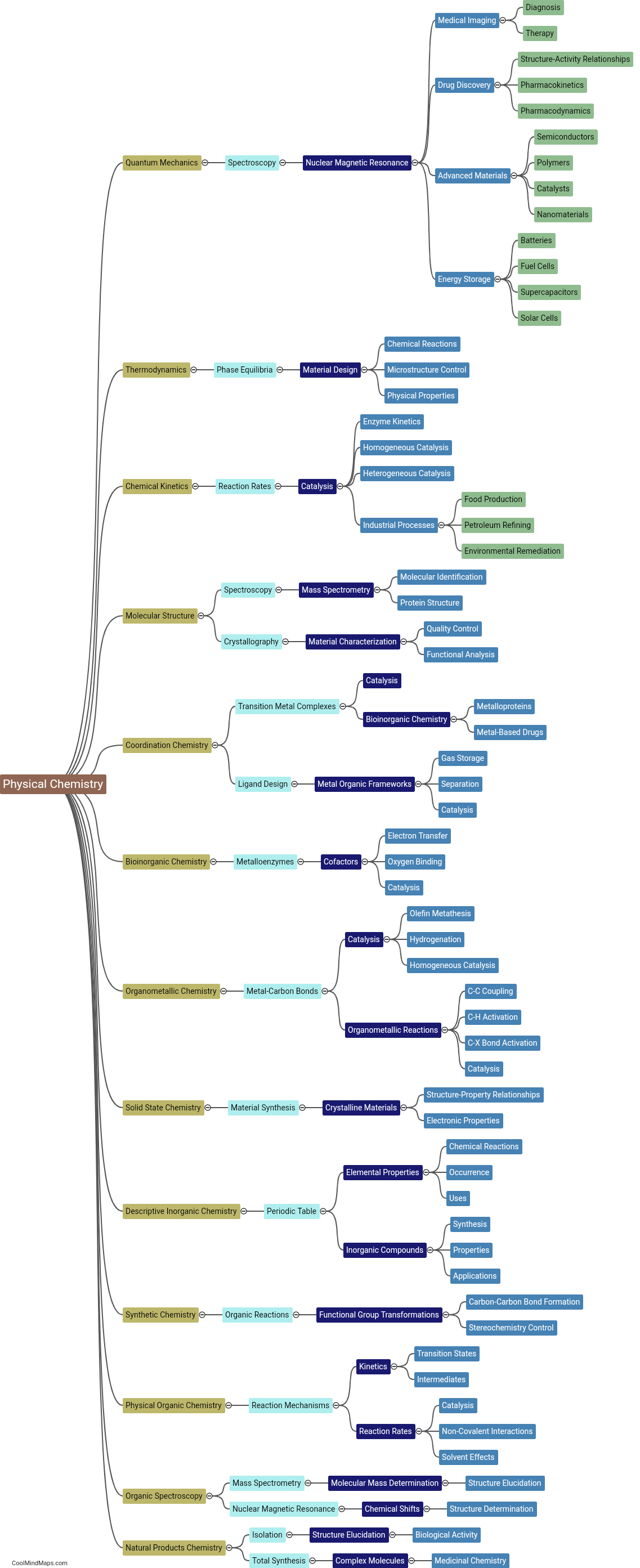
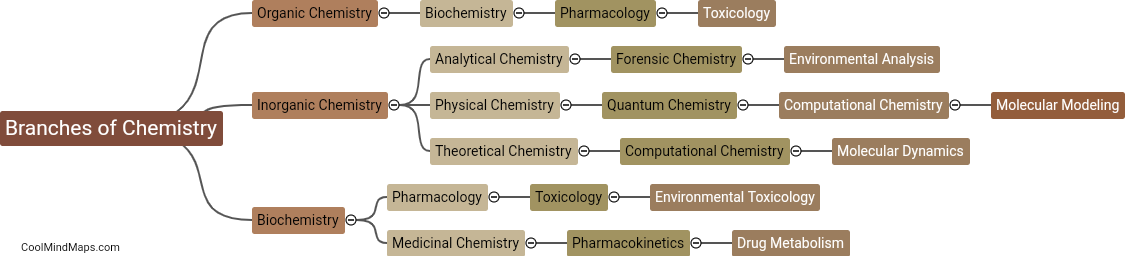
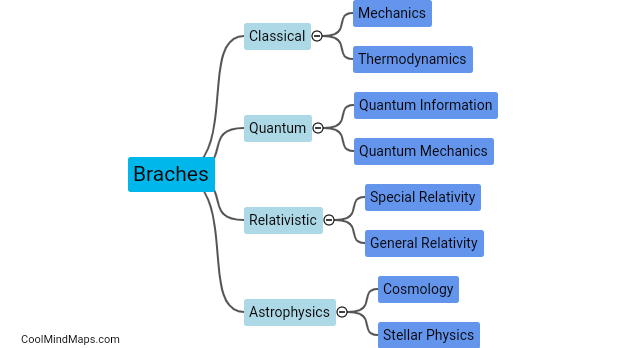
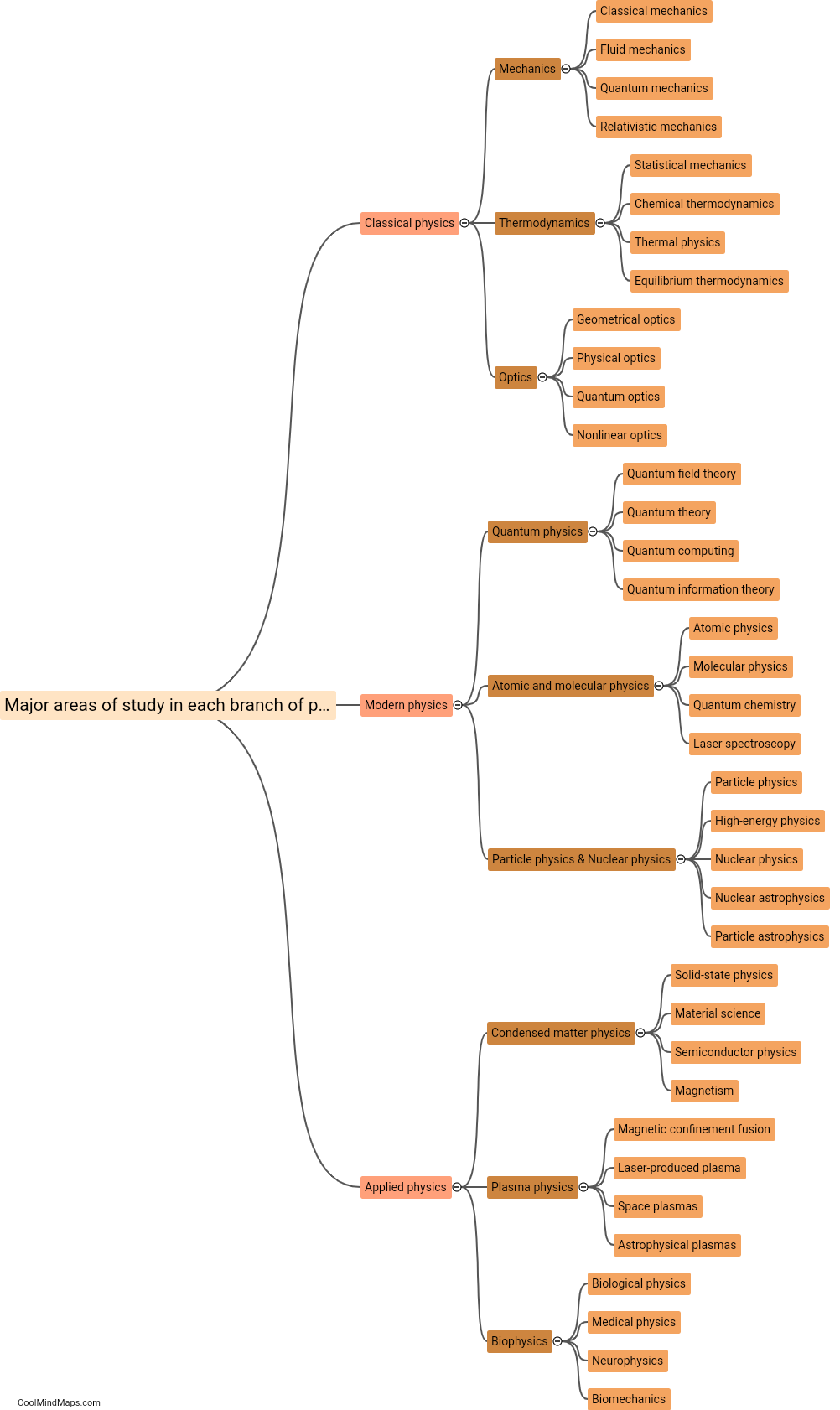
What are the key characteristics of each branch?
Each branch of government in a democratic system has distinct key characteristics. The executive branch, headed by the president or prime minister, is responsible for enforcing and implementing the laws passed by the legislative branch. It has the authority to make decisions, negotiate treaties, and command the military. The legislative branch, typically comprising a parliament or congress, is responsible for making laws. It consists of elected representatives who discuss, debate, and vote on proposed legislation. Lastly, the judicial branch is responsible for interpreting and applying the laws. It consists of courts and judges who ensure the constitutionality of legislation and settle disputes between individuals or the government. The judiciary is independent, impartial, and gives the final interpretation of the law. These key characteristics of each branch ensure a system of checks and balances, preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful.
This mind map was published on 21 July 2023 and has been viewed 119 times.