What are the different types of cells?
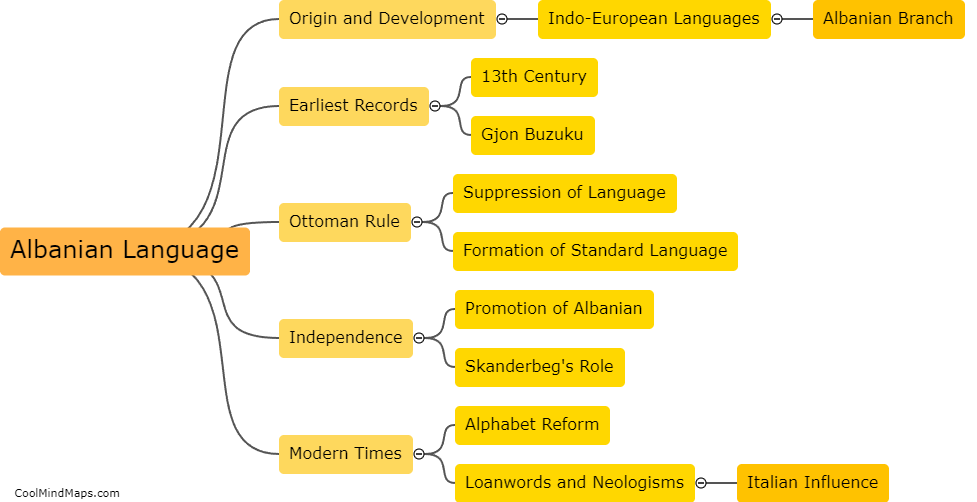
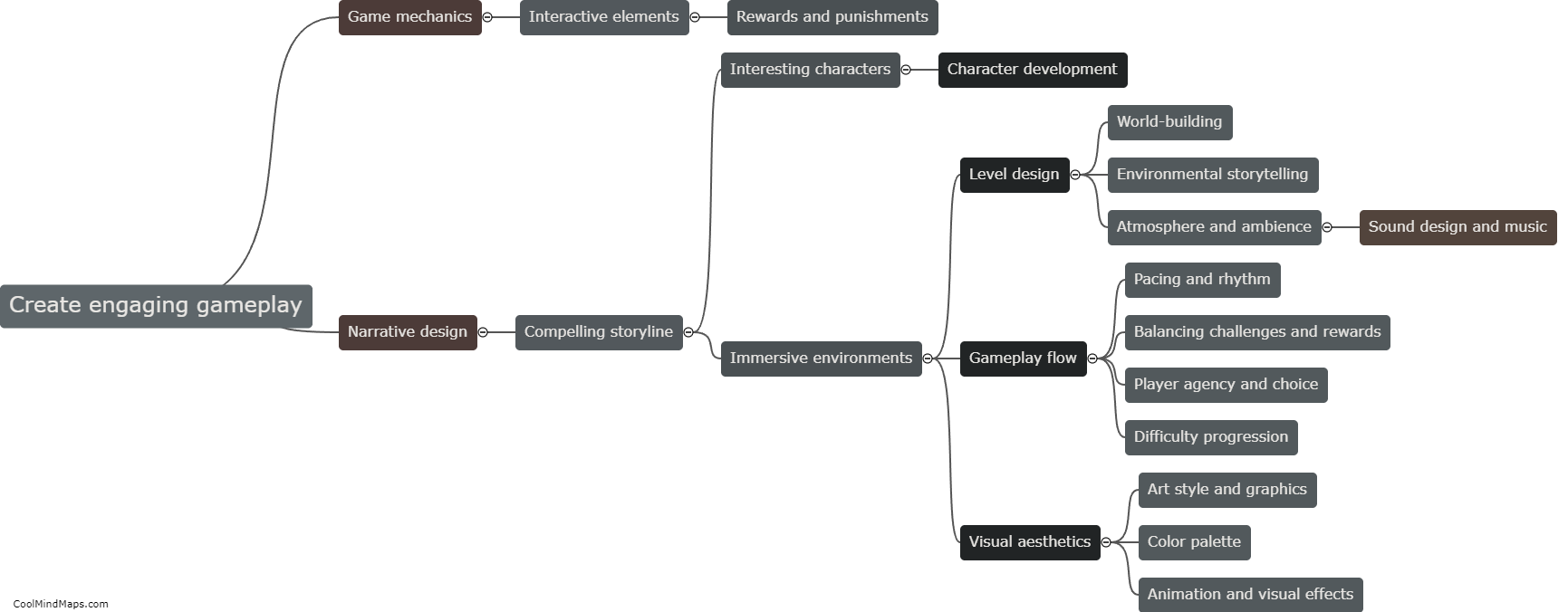
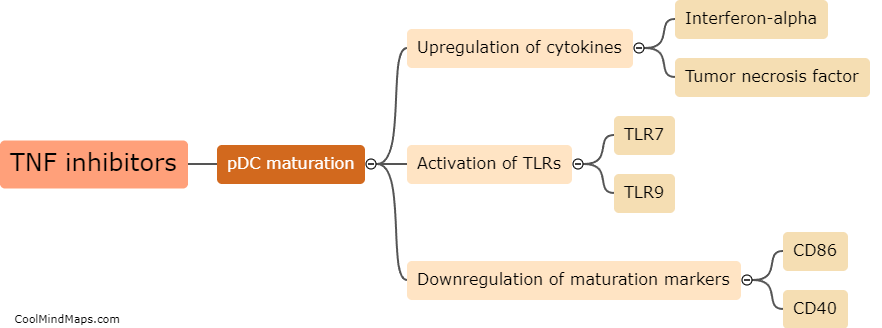
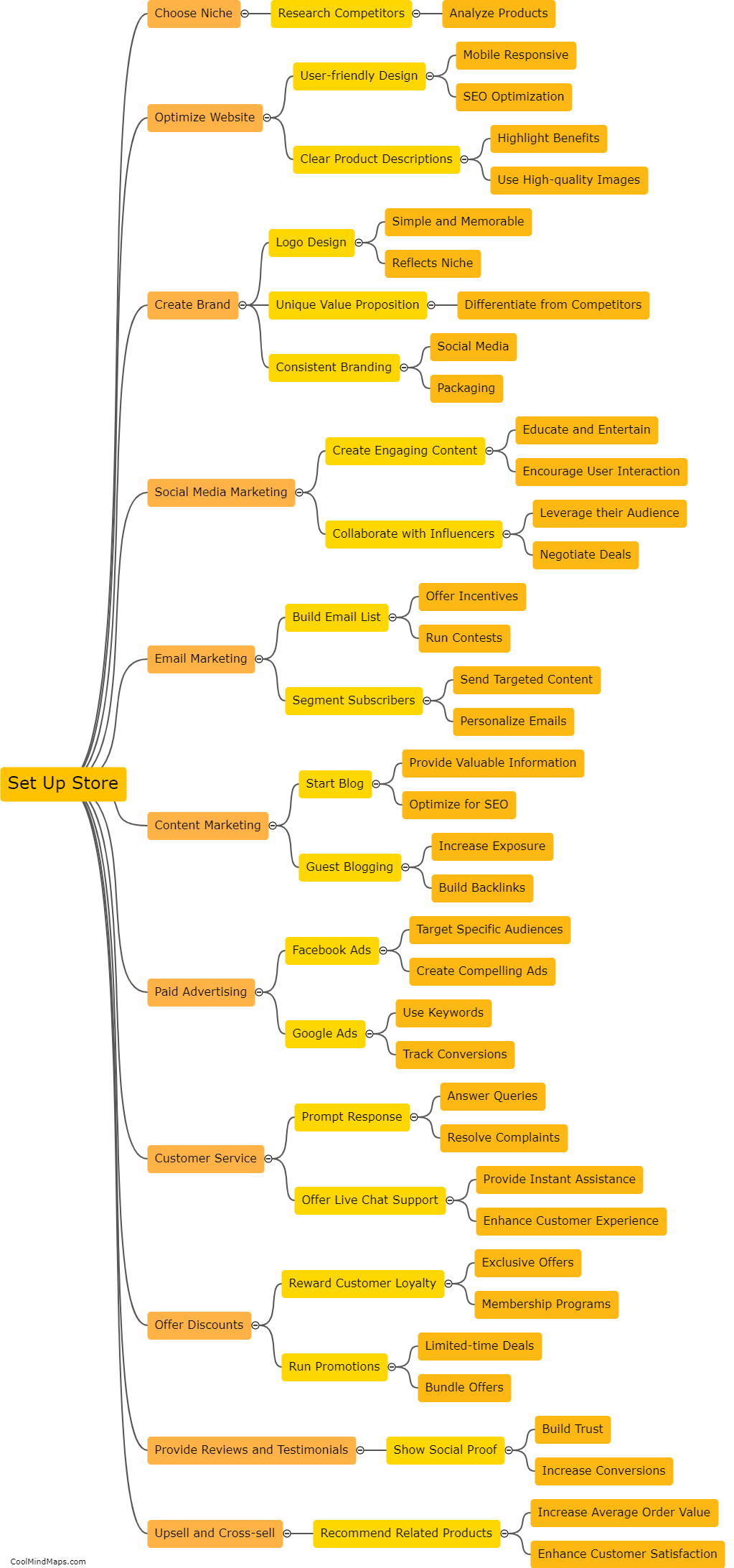
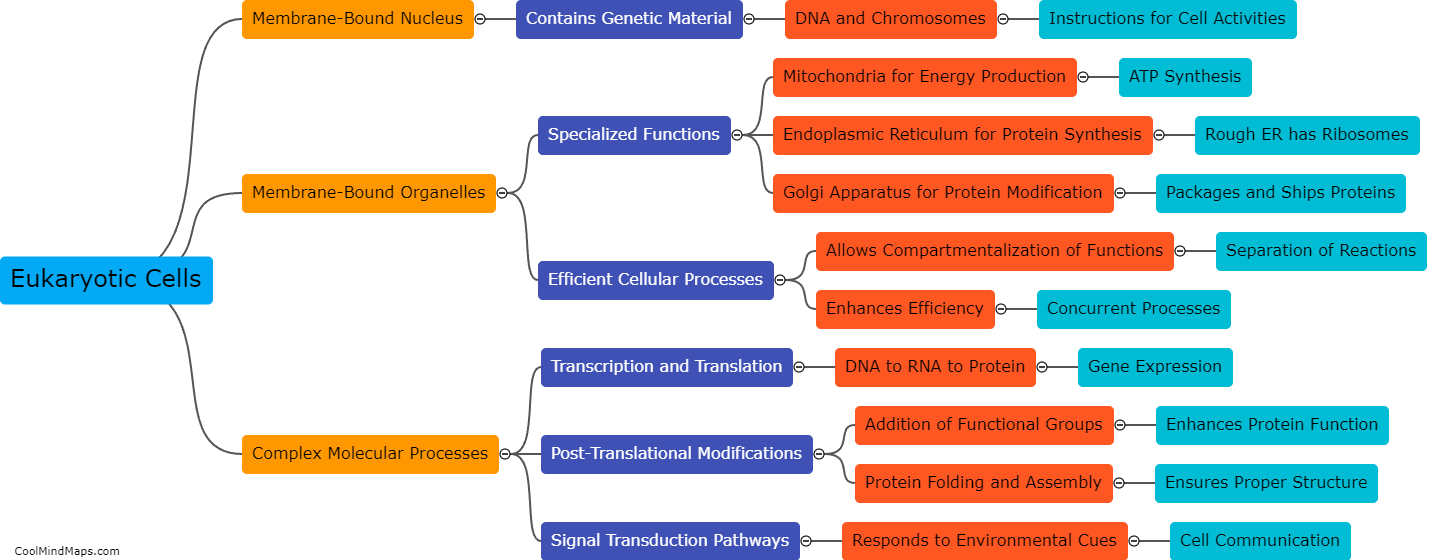
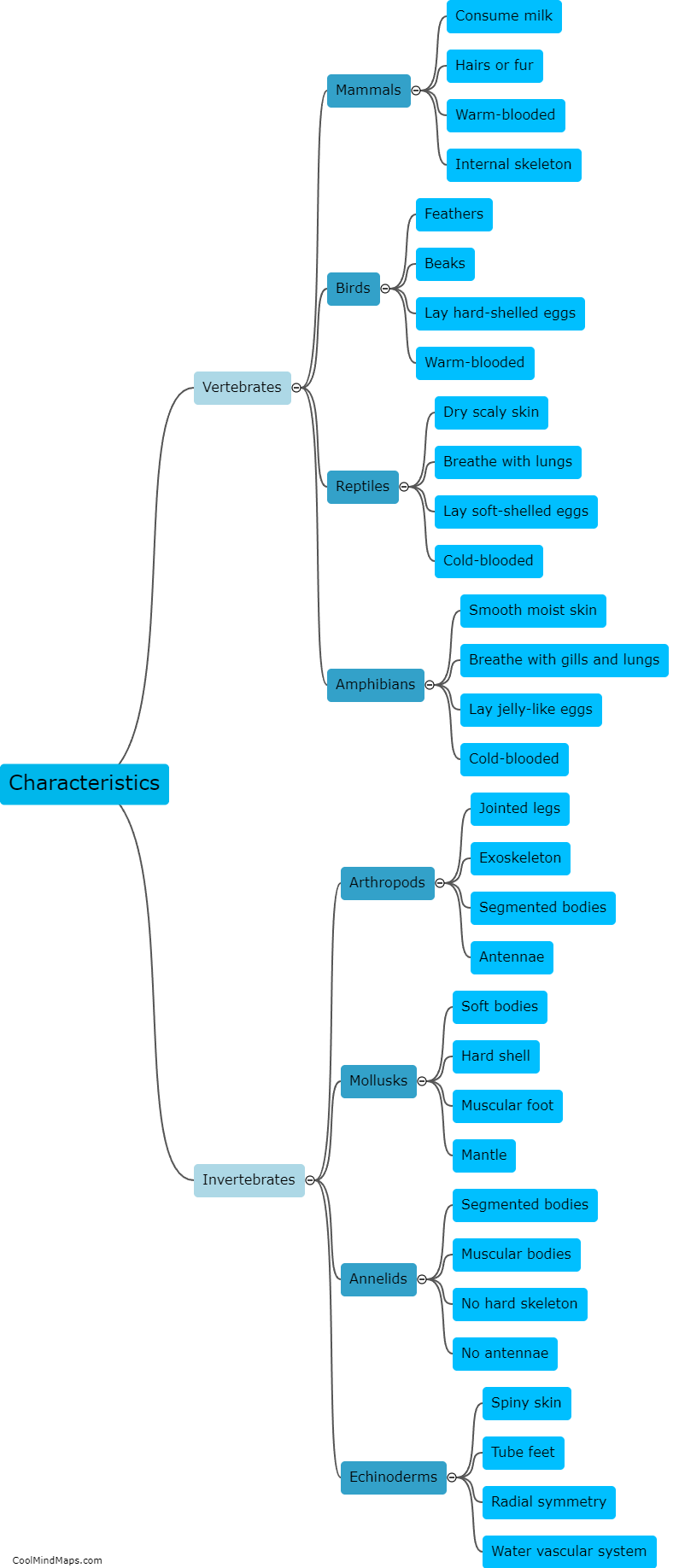
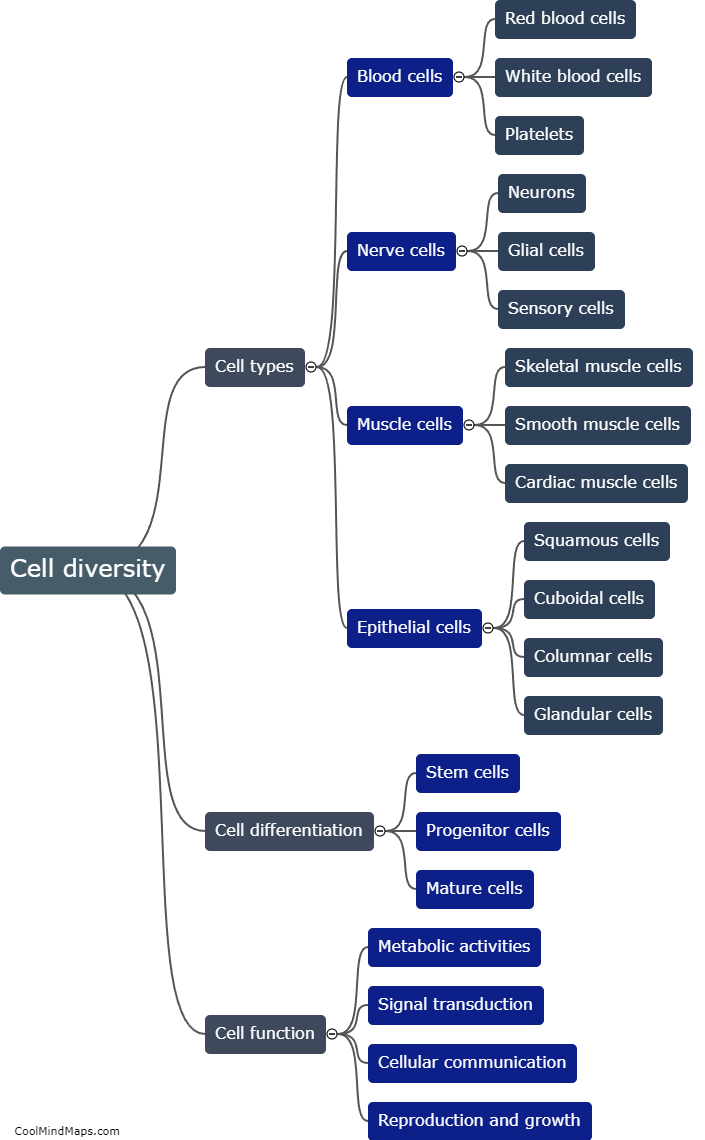
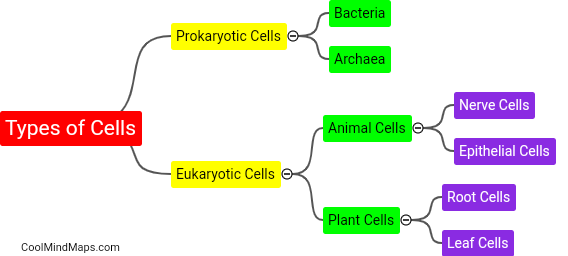
There are multiple types of cells in living organisms, each with distinct structures and functions. The most fundamental type is the prokaryotic cell, which lacks a nucleus and organelles. It is found in bacteria and archaea. On the other hand, eukaryotic cells, found in animals, plants, fungi, and protists, have a nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can further be categorized into animal cells, plant cells, fungal cells, and protist cells based on their specific features and functions. Animal cells, for example, do not possess a cell wall, while plant cells have a rigid cell wall and chloroplasts for photosynthesis. Fungal cells have a cell wall made of chitin and may contain structures like hyphae and mycelium. Lastly, protist cells constitute a diverse group with various adaptations and may possess features of animal, plant, or fungal cells depending on their specific classification. The differentiation of cells into these diverse types allows for specialization and coordination in numerous biological processes.
This mind map was published on 18 October 2023 and has been viewed 106 times.