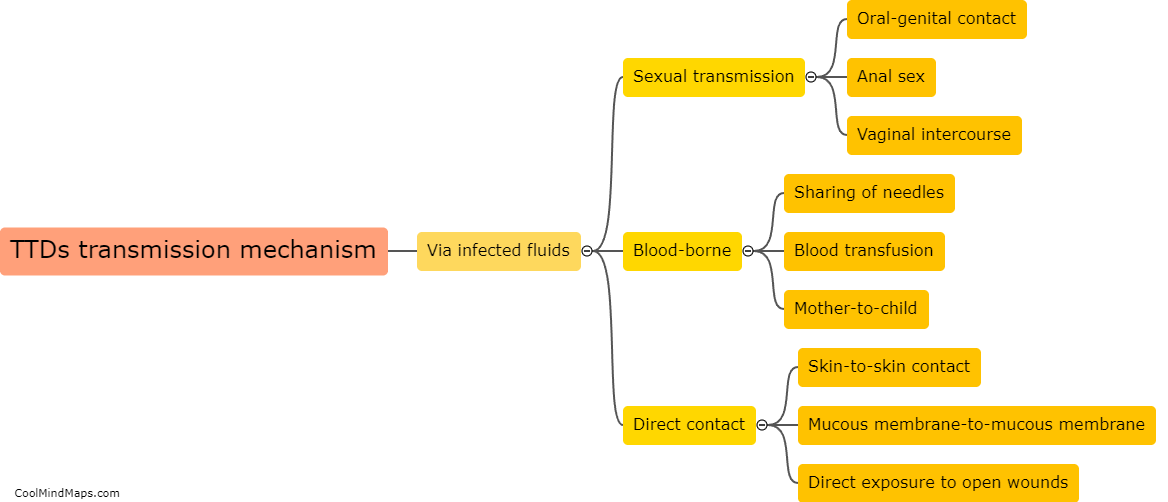
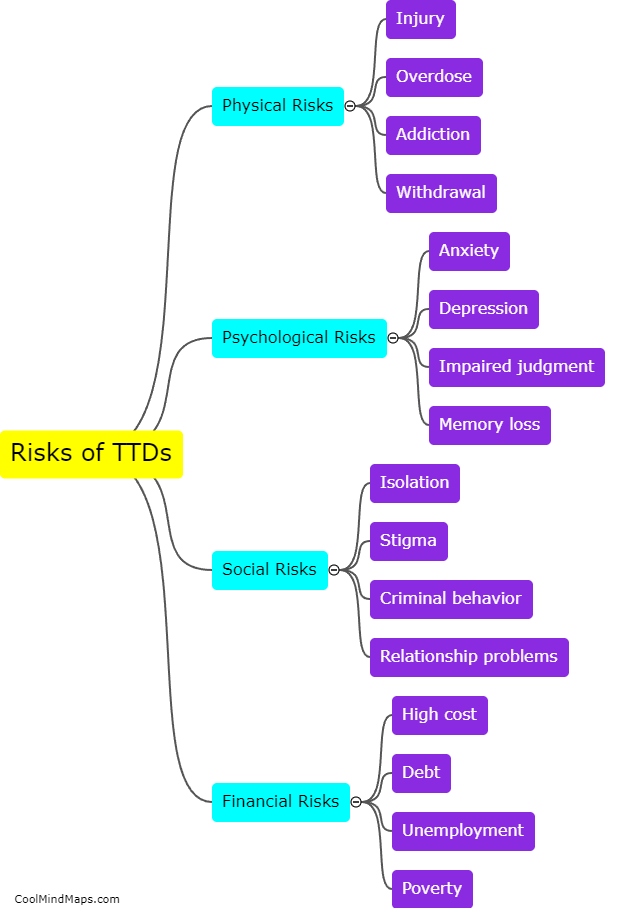
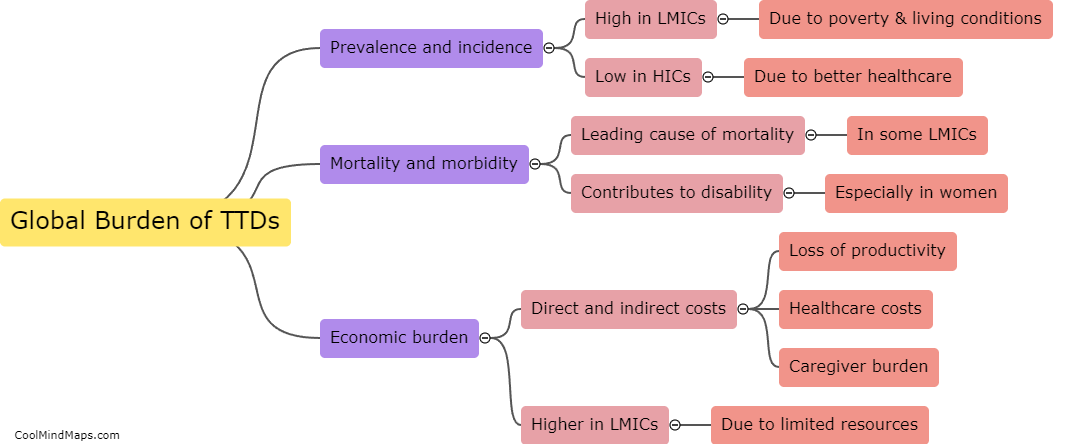
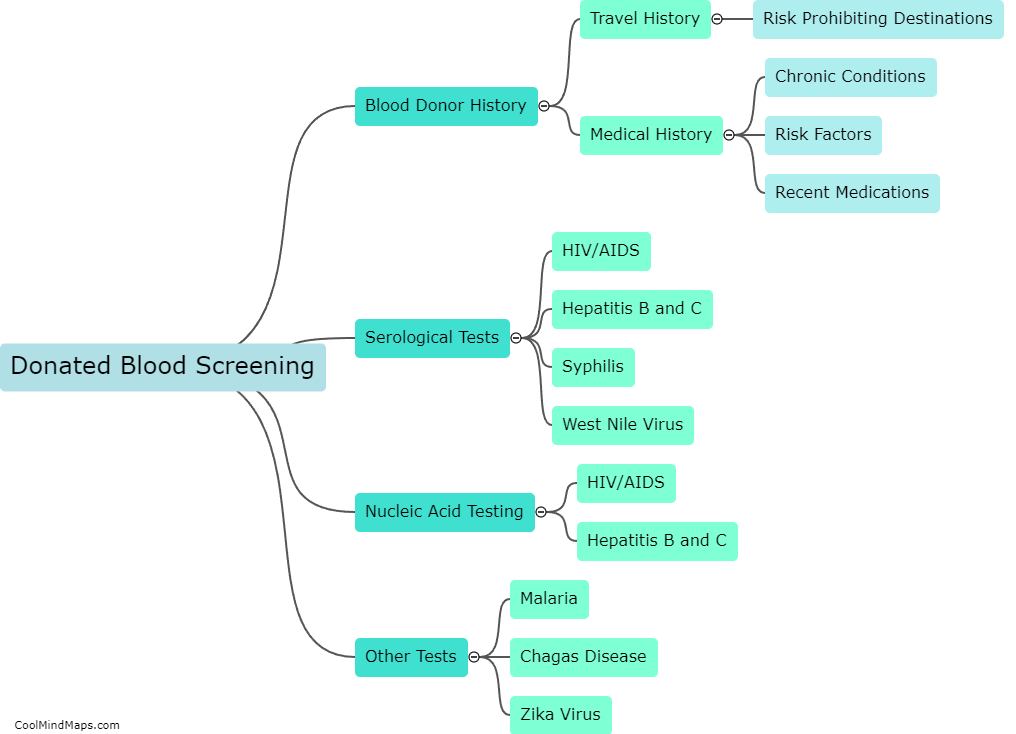
What is Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) and its limitations?
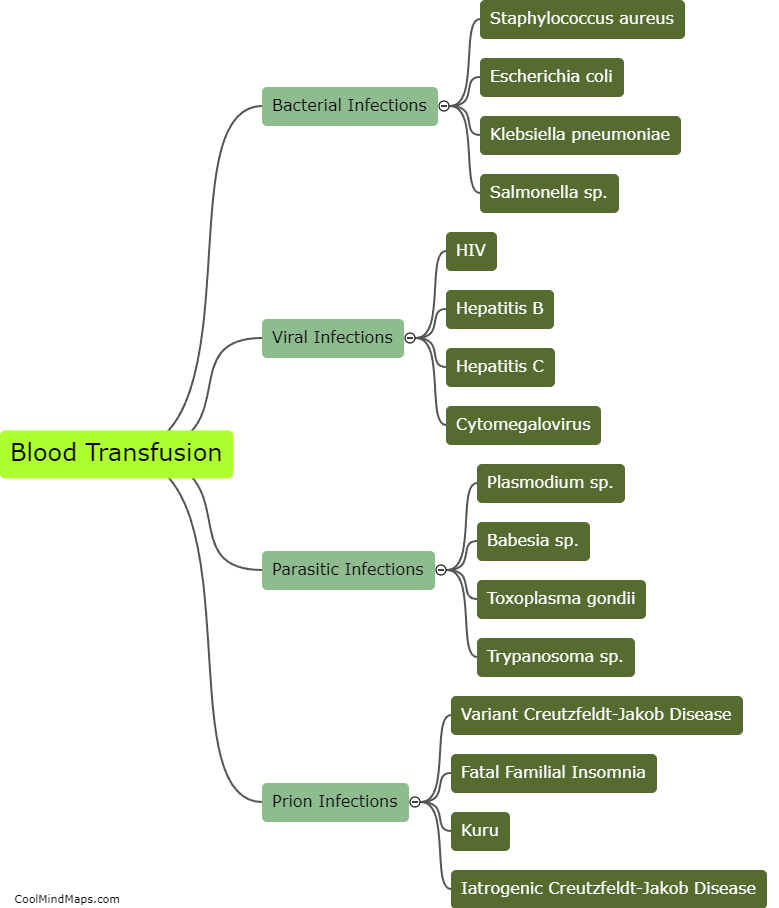
Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) is a laboratory technique that detects and amplifies genetic material (DNA or RNA) from viruses, bacteria, or parasites. NAT is commonly used for screening blood transfusions and organ donations, detecting sexually transmitted infections, and diagnosing viral infections such as HIV and hepatitis. However, NAT has some limitations. False-positive or false-negative results may occur due to contamination, technical errors, or mutation in the target gene. Hence, NAT results should always be interpreted by trained medical professionals and confirmed with other diagnostic tests. NAT is also relatively expensive and time-consuming compared to other diagnostic techniques.

This mind map was published on 25 June 2023 and has been viewed 104 times.