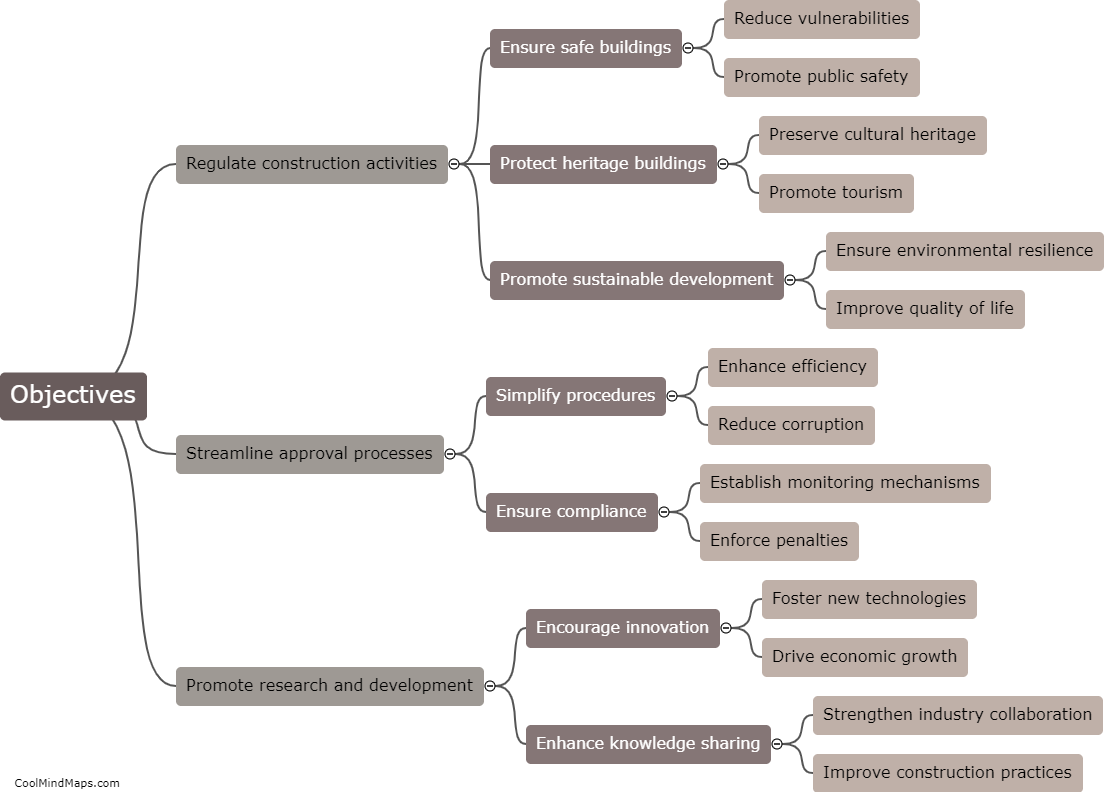
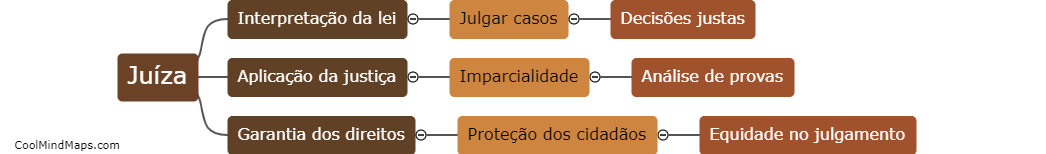
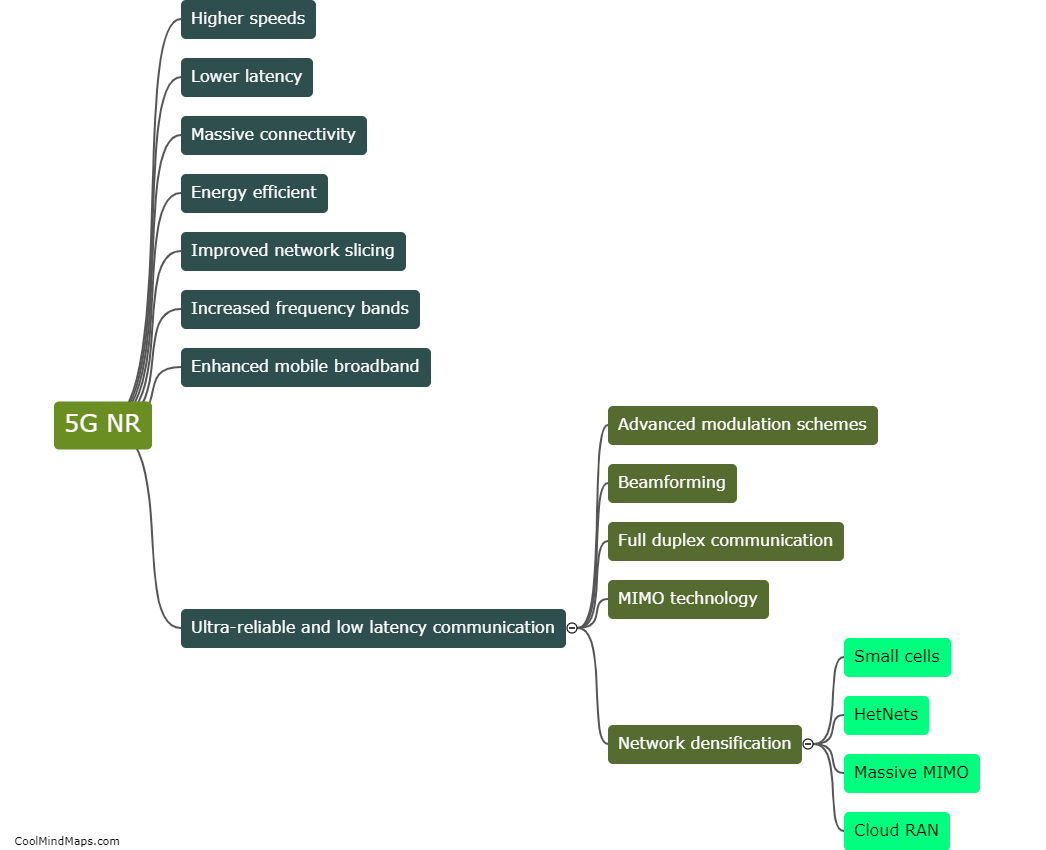
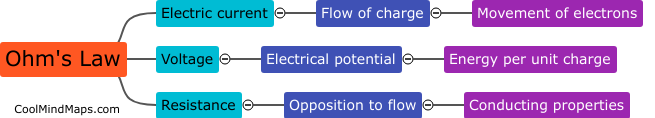
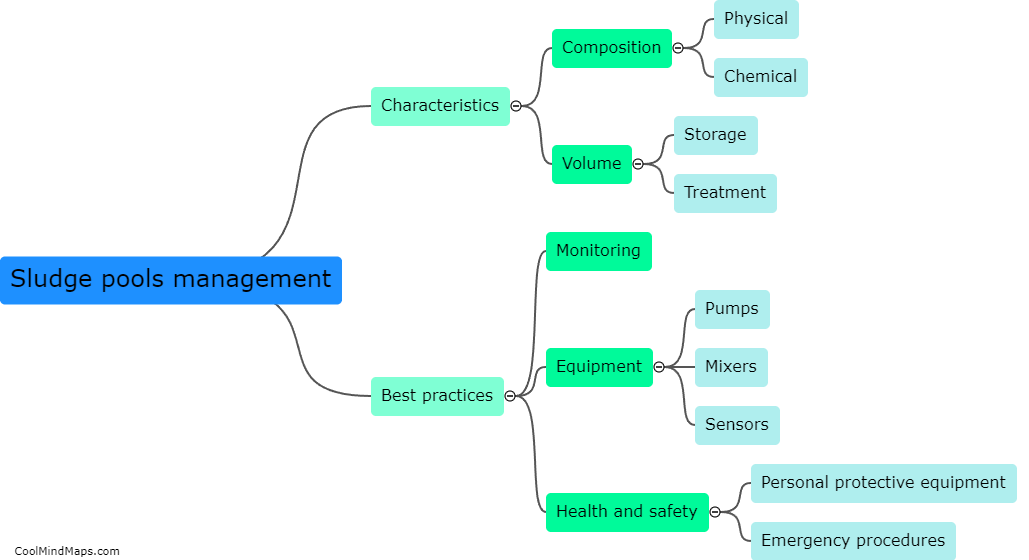
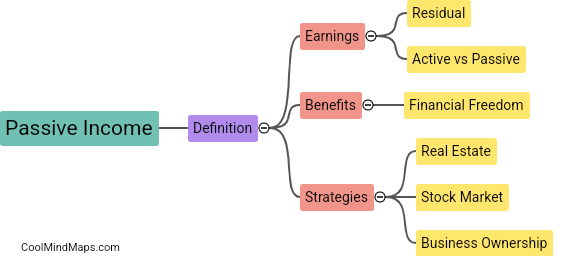
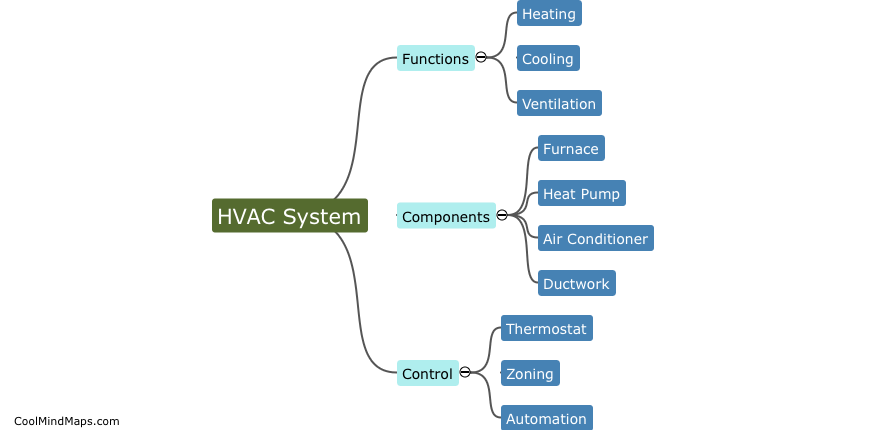
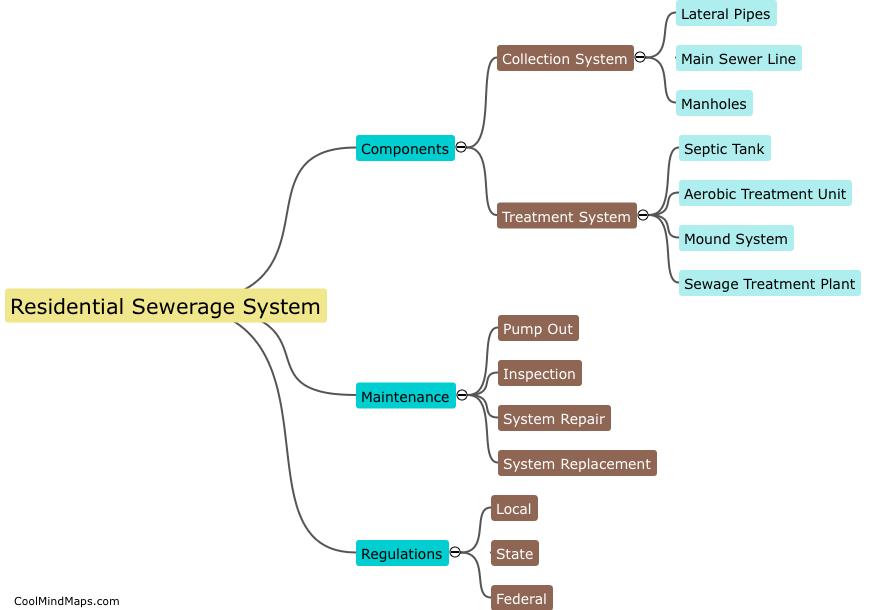
How does a residential water supply system work?
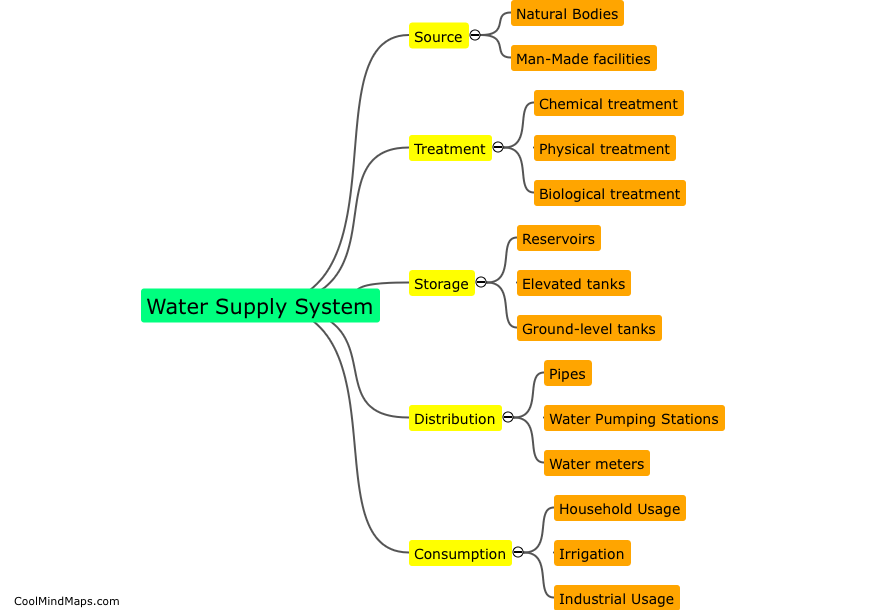
A residential water supply system typically consists of a network of pipes, valves, and fittings that are responsible for distributing fresh water to individual households. The process of water supply begins with the collection of water from natural sources such as lakes or rivers, which is then treated at a water treatment plant to ensure its purity. Once treated, the water is pumped into a distribution network that delivers it to individual homes through a system of pipes that are connected to a water meter. Water flowing through the network is typically controlled by valves that regulate the flow rate and pressure, while pumps may be used to boost water pressure if necessary. Within individual households, water is typically distributed through a series of pipes and fixtures such as faucets, showerheads, and toilets. Waste water generated by the household is typically collected and transported to a wastewater treatment plant for treatment before being released back into the environment.
This mind map was published on 18 April 2023 and has been viewed 104 times.