What is the basic structure of an SQL statement?
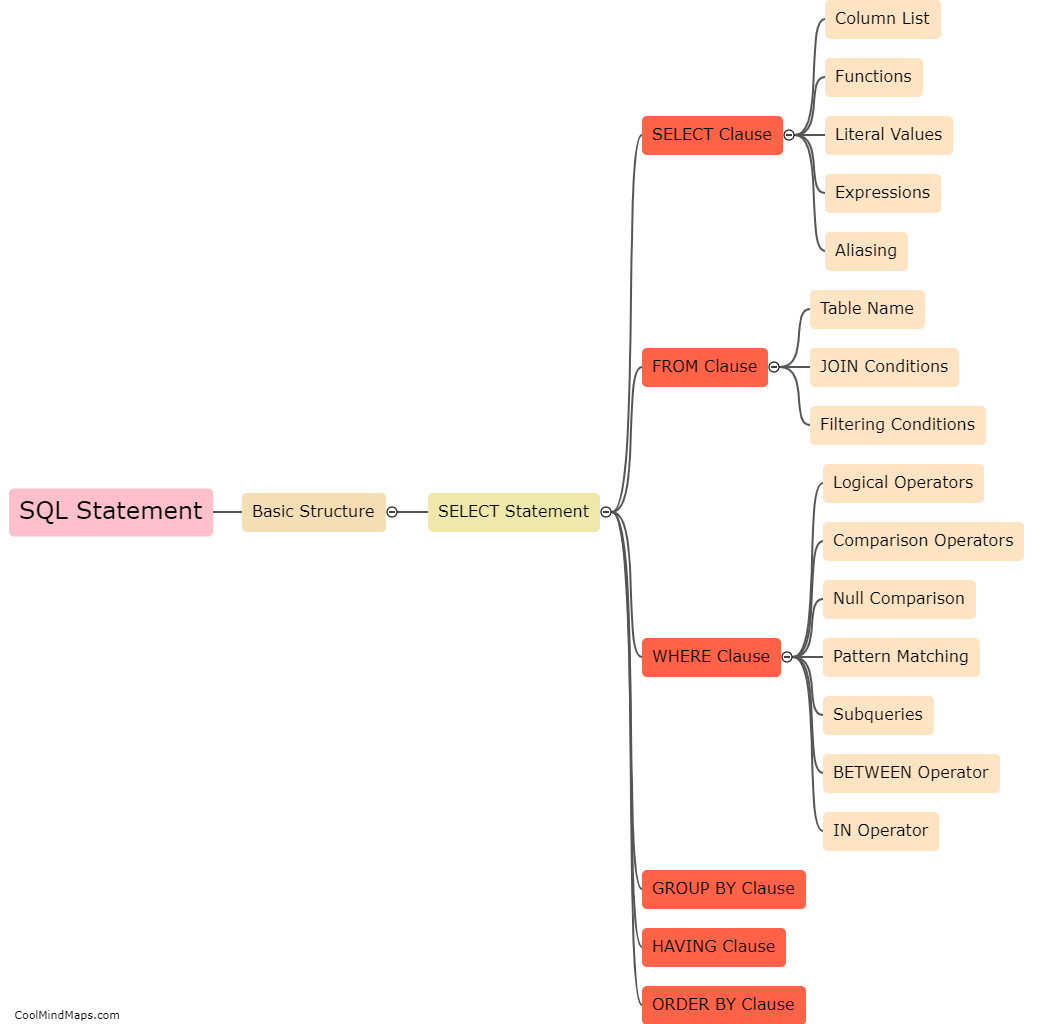
The basic structure of an SQL statement consists of three main components: the SELECT clause, the FROM clause, and the WHERE clause. The SELECT clause is used to specify the columns or data elements to be retrieved from the database. It begins with the keyword SELECT followed by a comma-separated list of column names or an asterisk (*) to select all columns. The FROM clause is used to specify the table or tables from which the data will be retrieved. It begins with the keyword FROM followed by the table name. Lastly, the WHERE clause is used to specify the conditions that must be met for a row to be included in the result set. It begins with the keyword WHERE followed by the condition or conditions. Together, these three components form the basic structure of an SQL statement which is used to query and retrieve data from a database.
This mind map was published on 7 January 2024 and has been viewed 149 times.