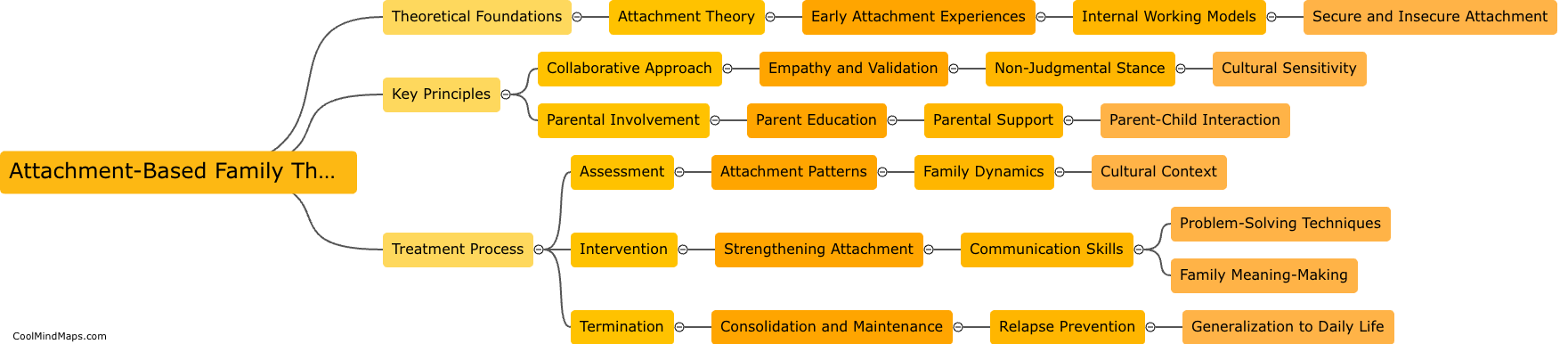
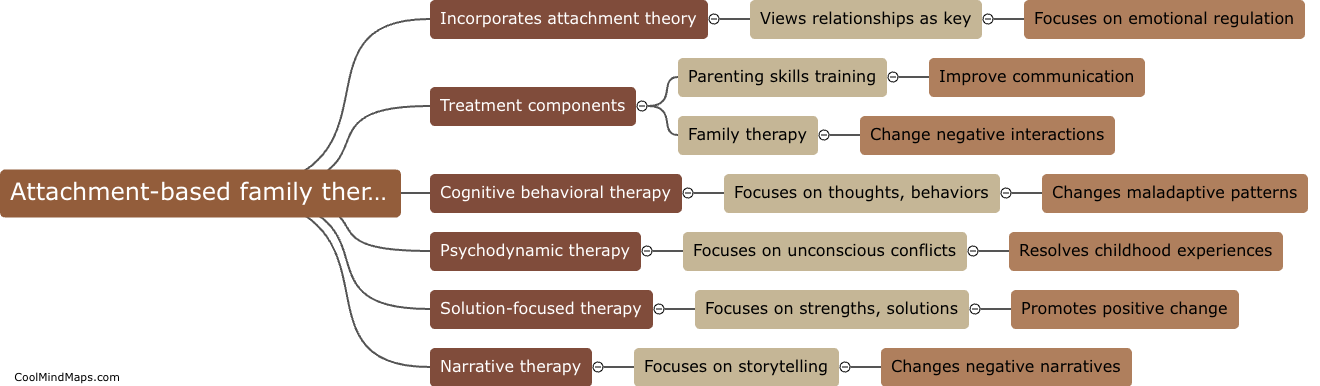
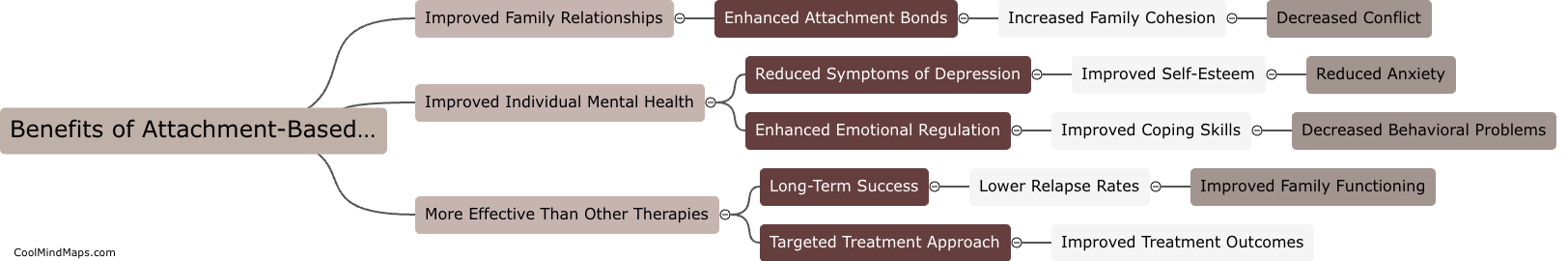
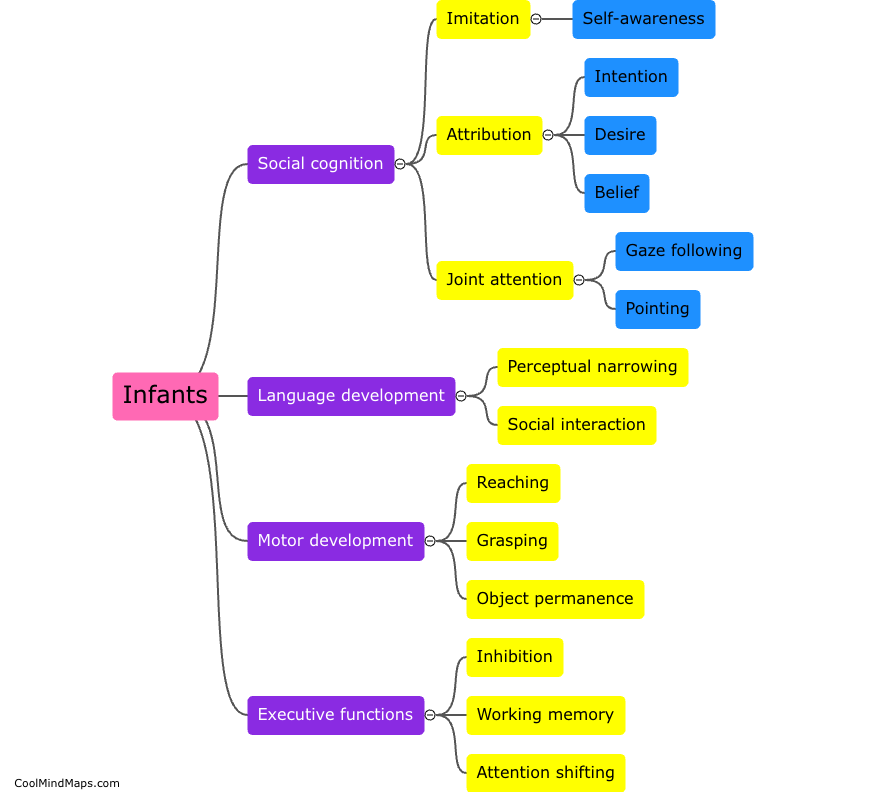
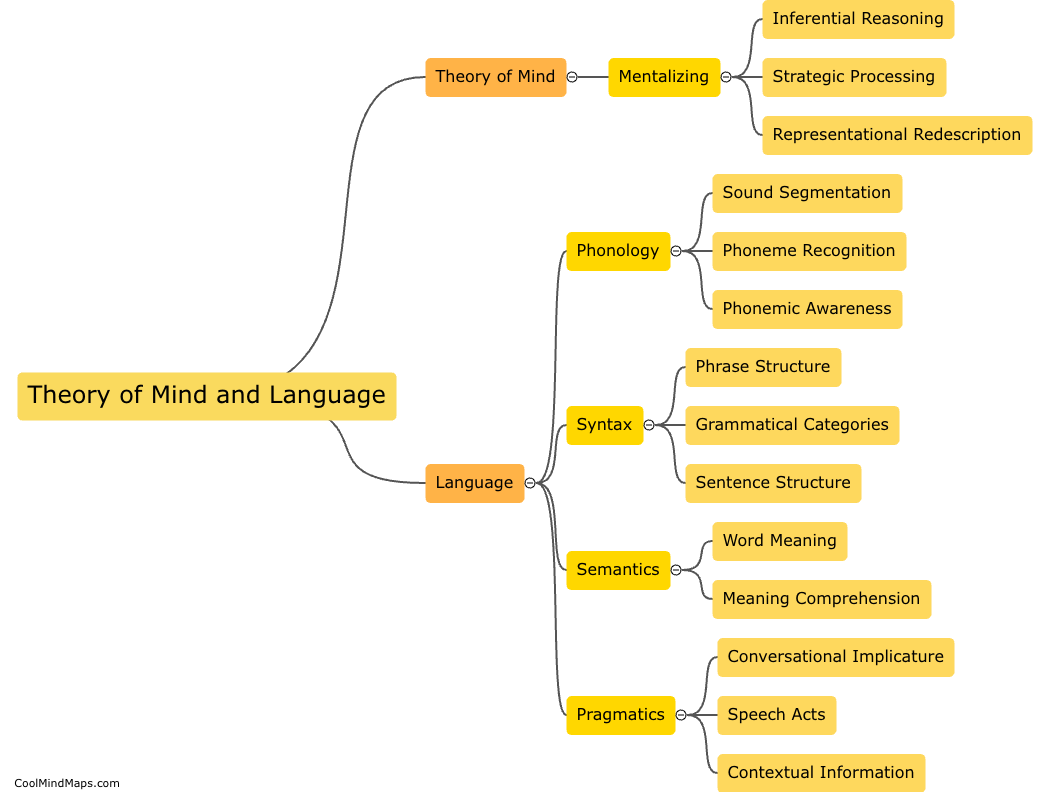
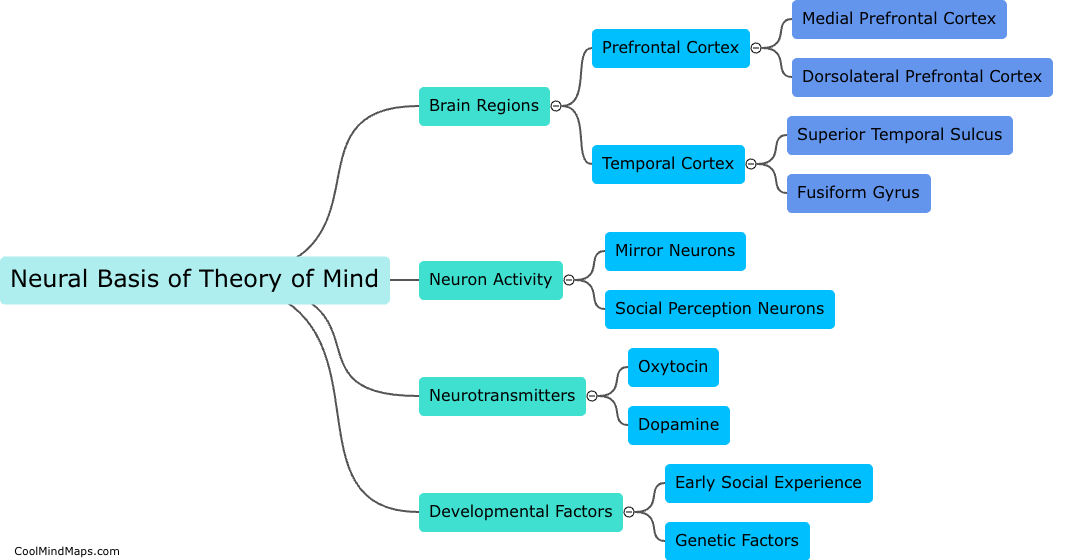
What is the neural basis of theory of mind?
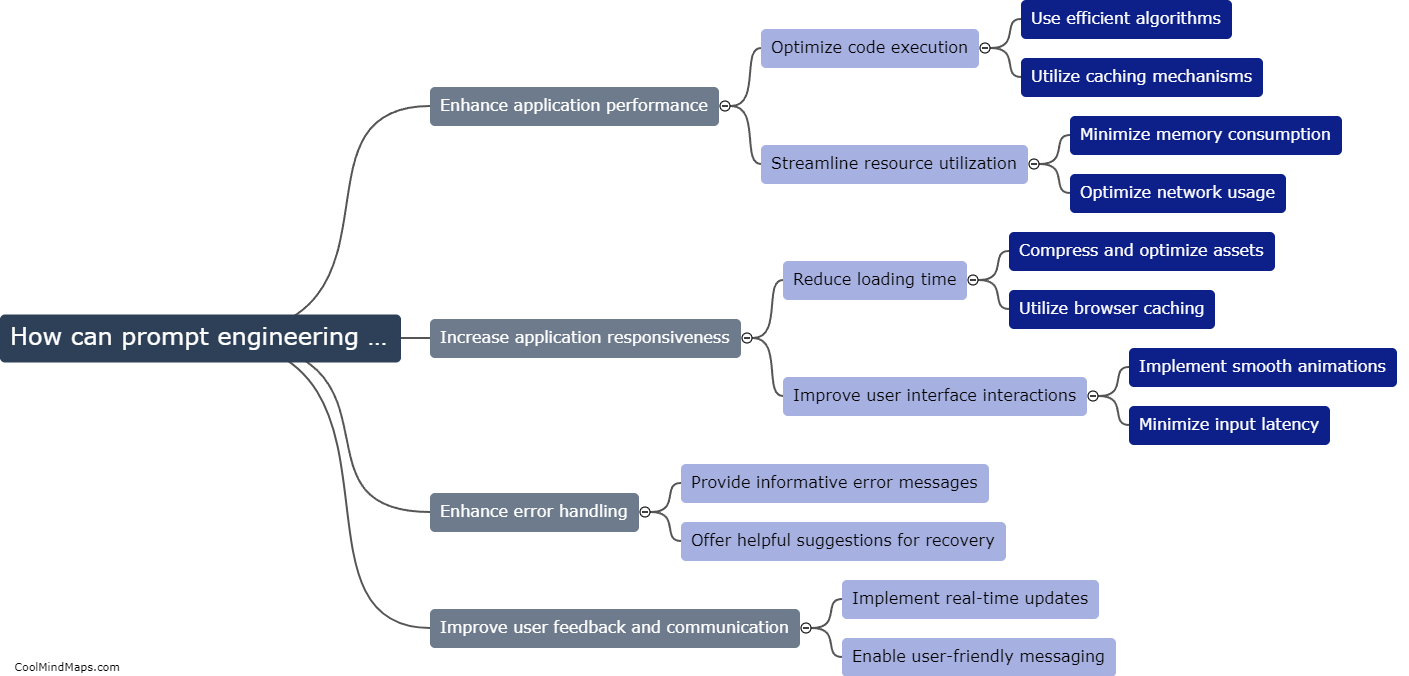
The neural basis of theory of mind refers to the brain regions and neural processes that underlie our ability to attribute mental states to others and understand their perspectives. Research has identified several brain regions involved in theory of mind, including the prefrontal cortex, temporal cortex, and temporoparietal junction. These regions are involved in a range of cognitive processes such as mentalizing, perspective-taking, and empathy, and have been shown to be active during tasks that require understanding the beliefs, desires, and intentions of others. Understanding the neural basis of theory of mind is important for advancing our understanding of social cognition and potentially treating disorders in which difficulties in understanding others' mental states are a core symptom, such as autism spectrum disorder.
This mind map was published on 4 June 2023 and has been viewed 114 times.