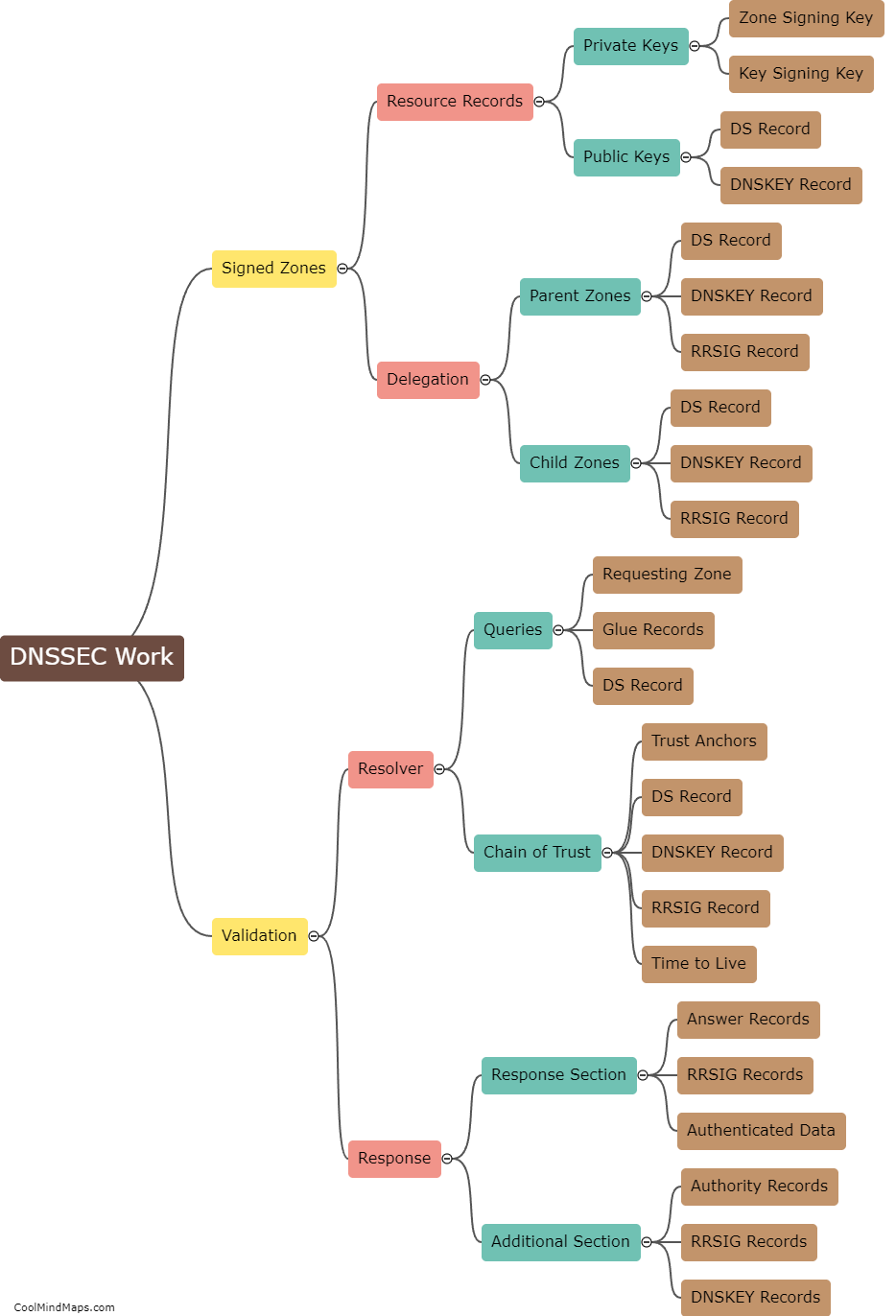
How does DNSSEC work?
DNSSEC, which stands for Domain Name System Security Extensions, is a technology that enhances the security of the Domain Name System (DNS). It works by adding digital signatures to DNS data to ensure its authenticity and integrity. DNSSEC utilizes public key cryptography, where a domain owner signs their DNS records using a private key, and this signature is verified by using the corresponding public key stored in the DNS root zone. These signatures create a chain of trust that extends down from the root zone to the authoritative DNS servers. When a user requests a DNS record, the server provides the record along with the digital signature. The client then verifies the signature using the public key to authenticate the response and ensure that the data hasn't been tampered with during transmission. By implementing DNSSEC, the risk of DNS-based attacks such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning is mitigated, providing a more secure and reliable DNS infrastructure.
This mind map was published on 10 November 2023 and has been viewed 97 times.