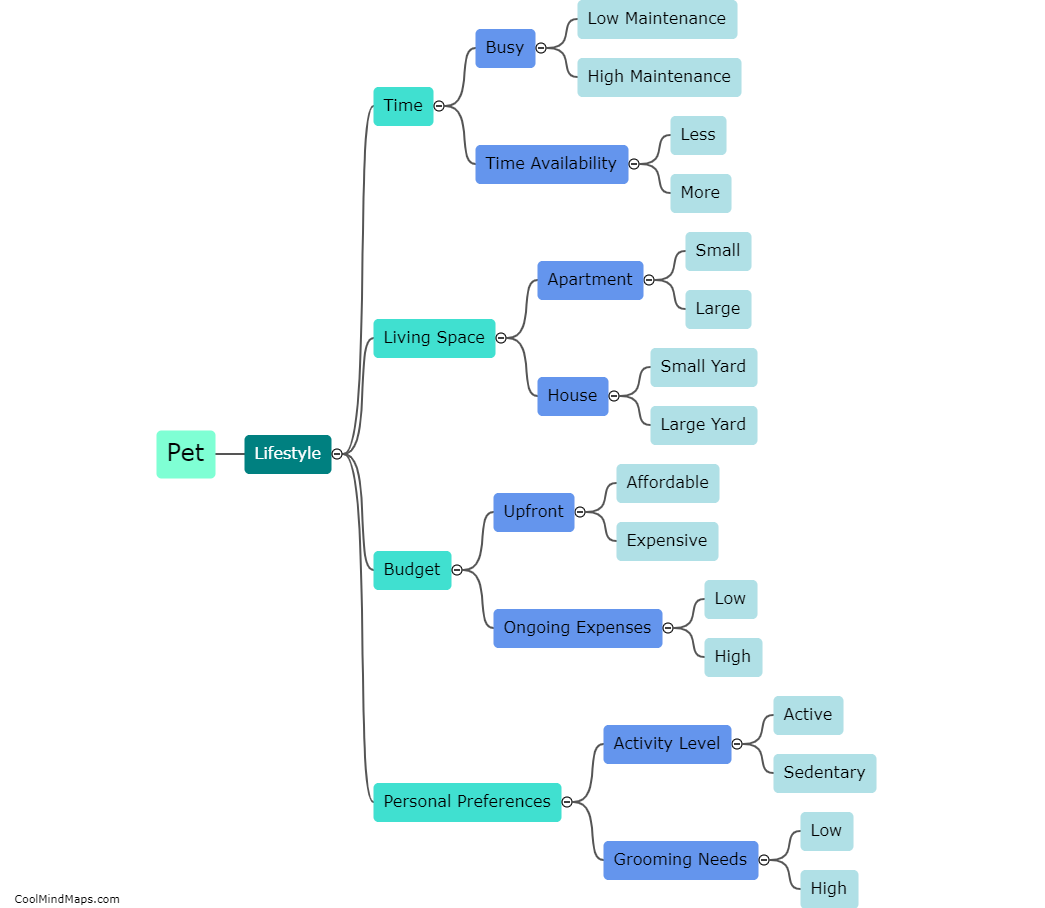
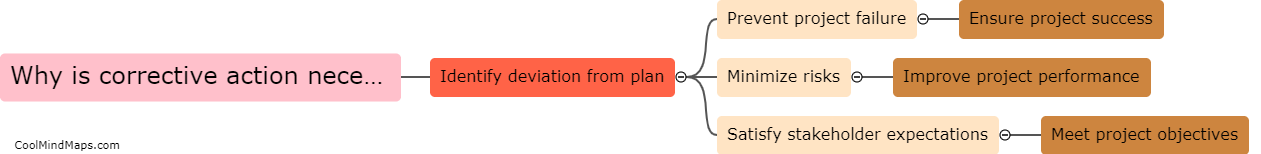
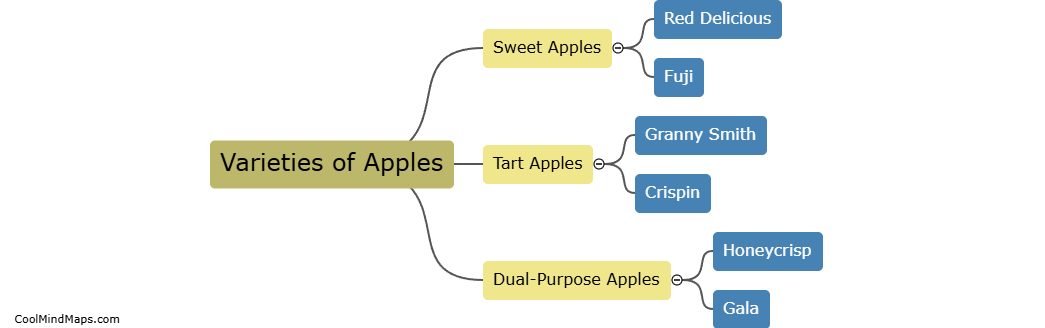
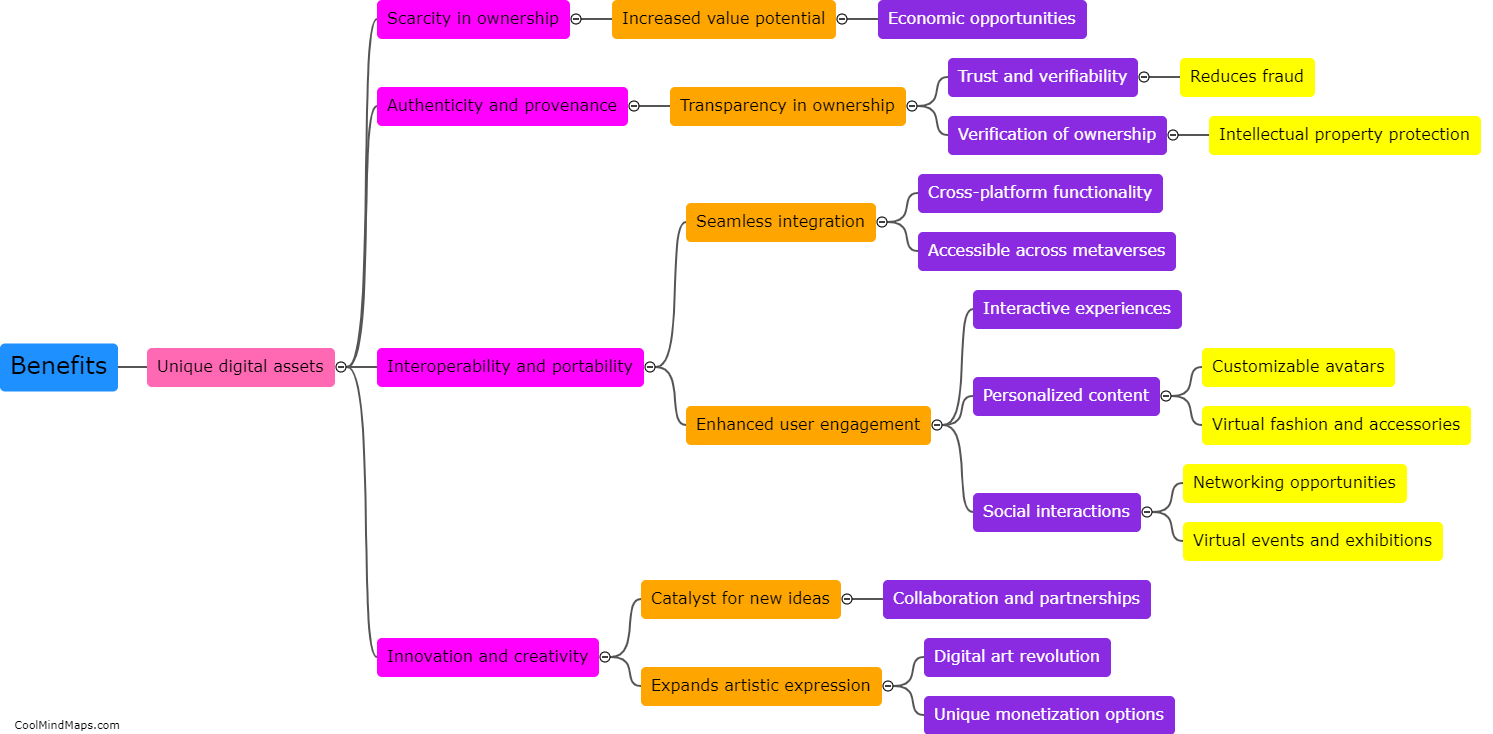
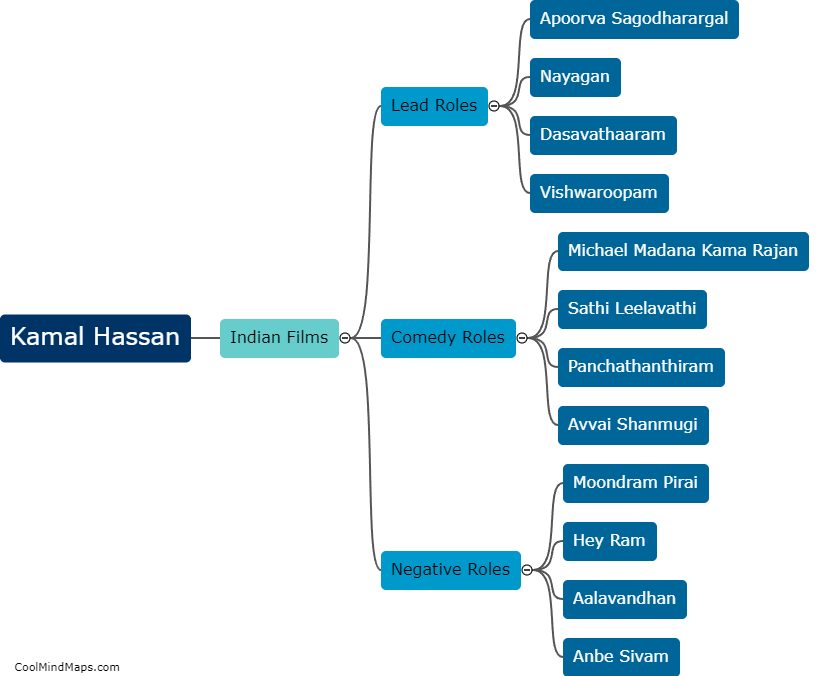
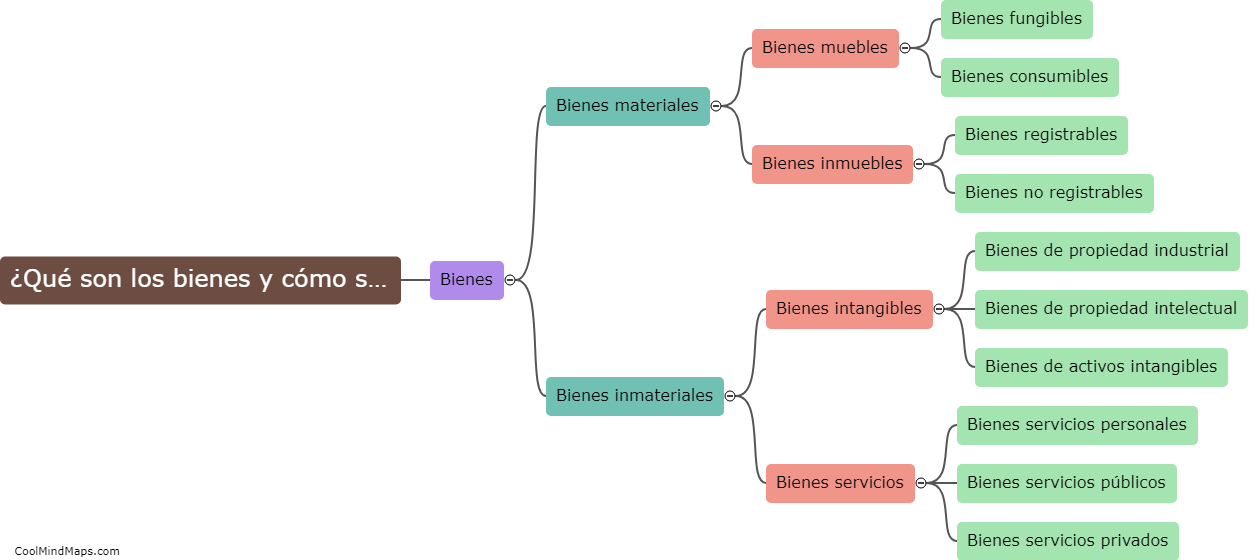
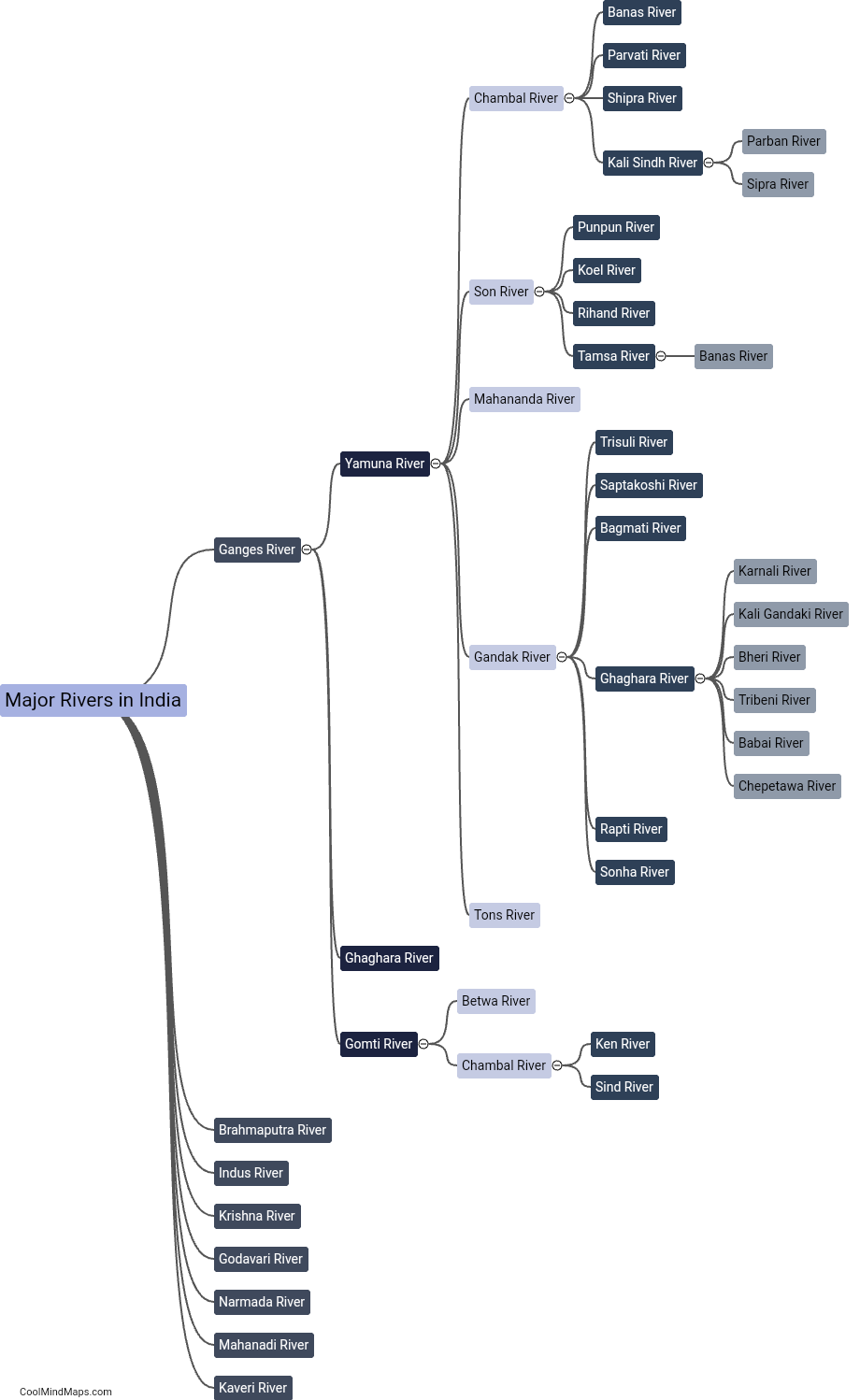
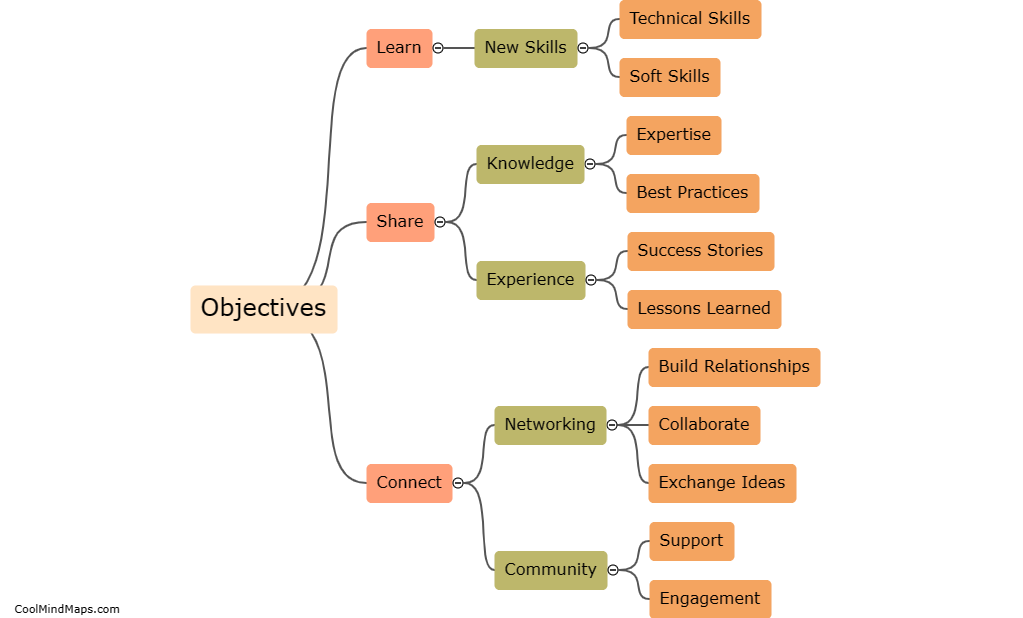
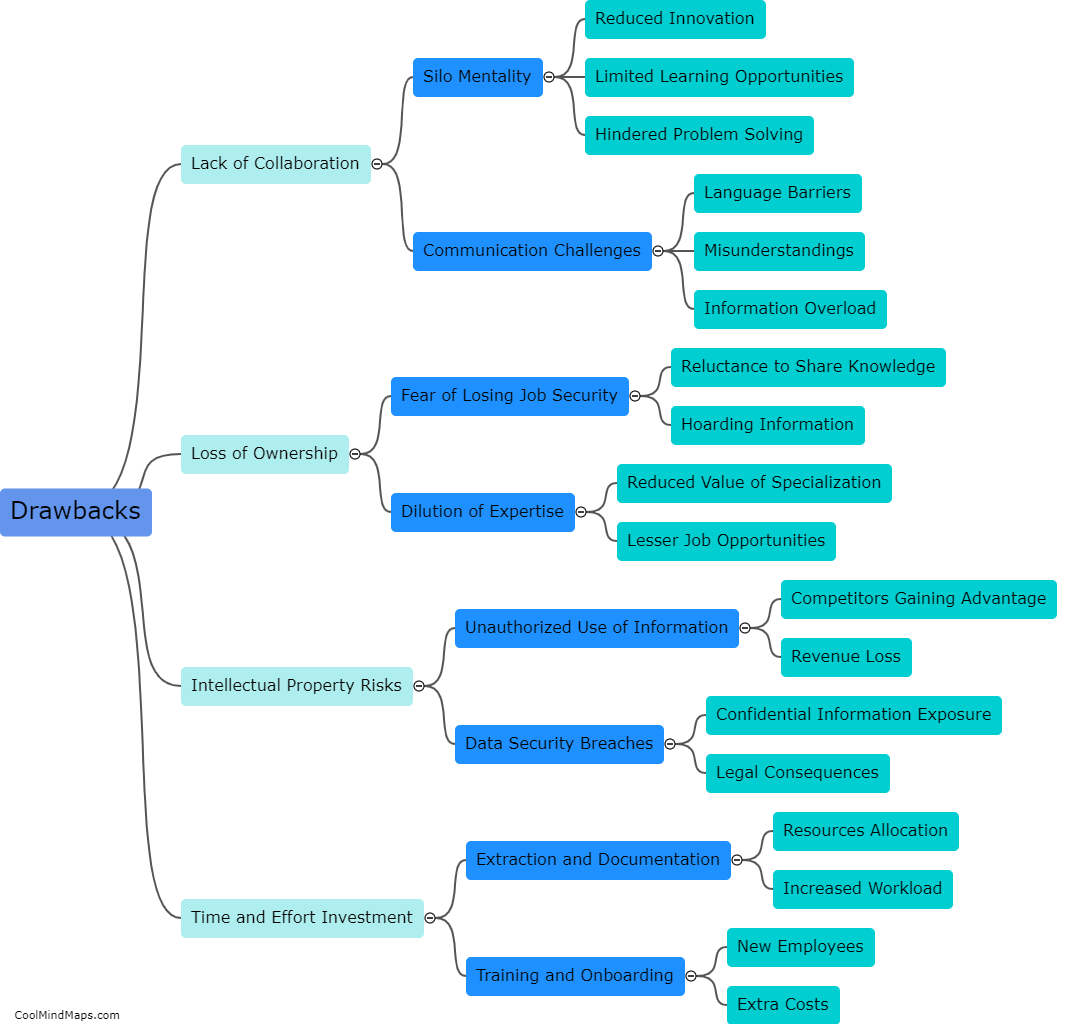
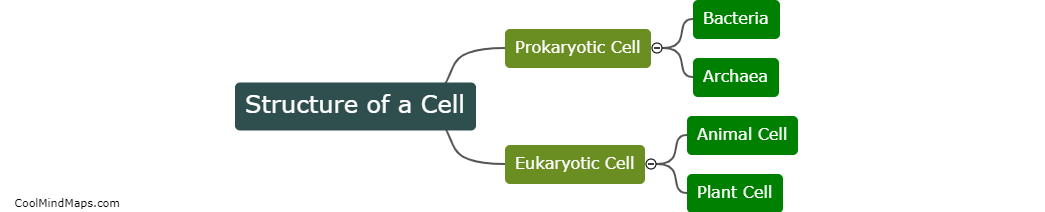
What is the structure of a cell?
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It is composed of various components that work together to carry out the essential processes required for life. The structure of a cell can be broadly divided into two main categories: the plasma membrane and the intracellular organelles. The plasma membrane forms the outer boundary of the cell, providing a protective barrier and governing the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Within the cell, organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes play critical roles in various cellular functions. These organelles are enclosed by membranes and have specific functions such as genetic control, energy production, protein synthesis, and waste disposal, respectively. Additionally, cells also contain cytoplasm, a jelly-like substance that fills the cell, and a variety of smaller structures known as cytoskeleton, which help maintain the cell's shape and enable cellular movement. Overall, the structure of a cell is highly organized and compartmentalized, ensuring proper functioning and survival of the organism.
This mind map was published on 3 December 2023 and has been viewed 103 times.