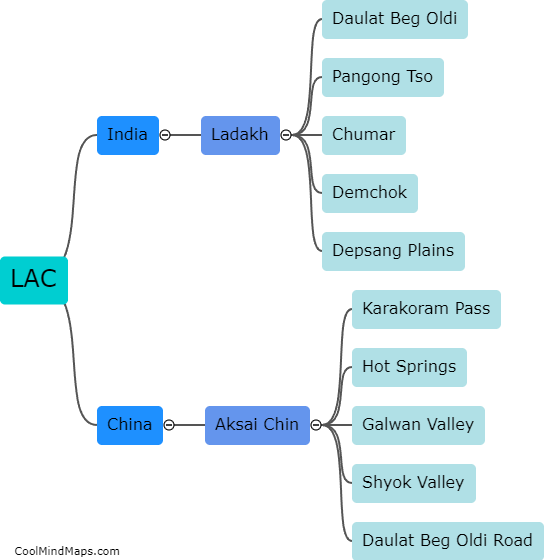
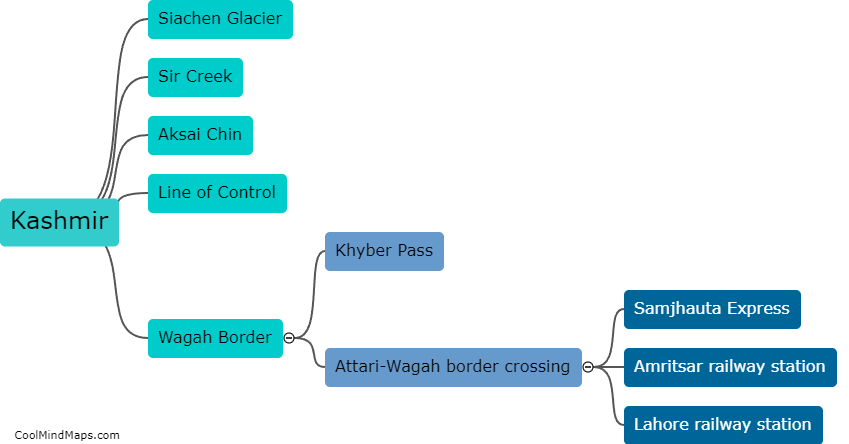
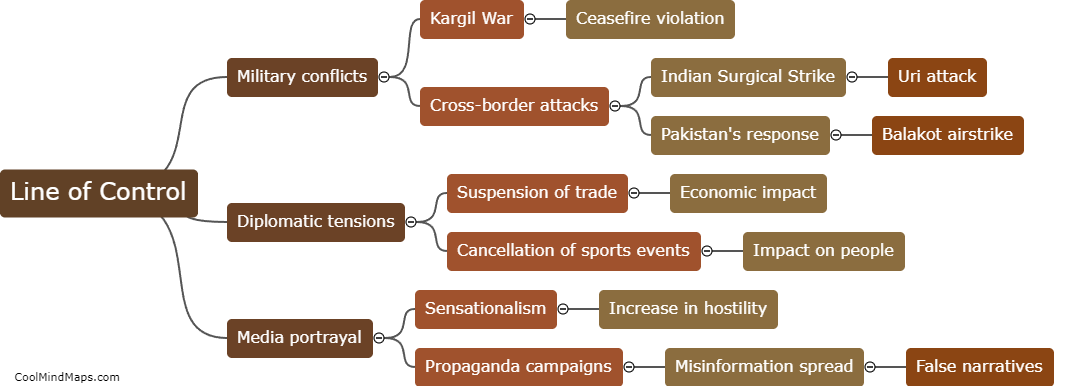
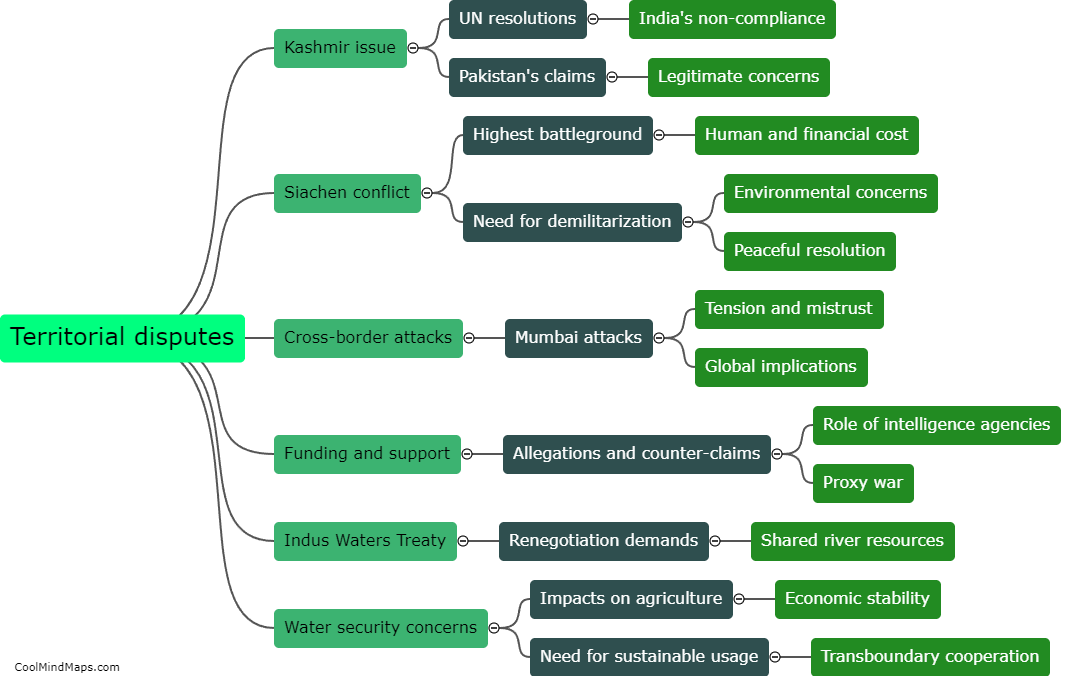
What are microRNAs?
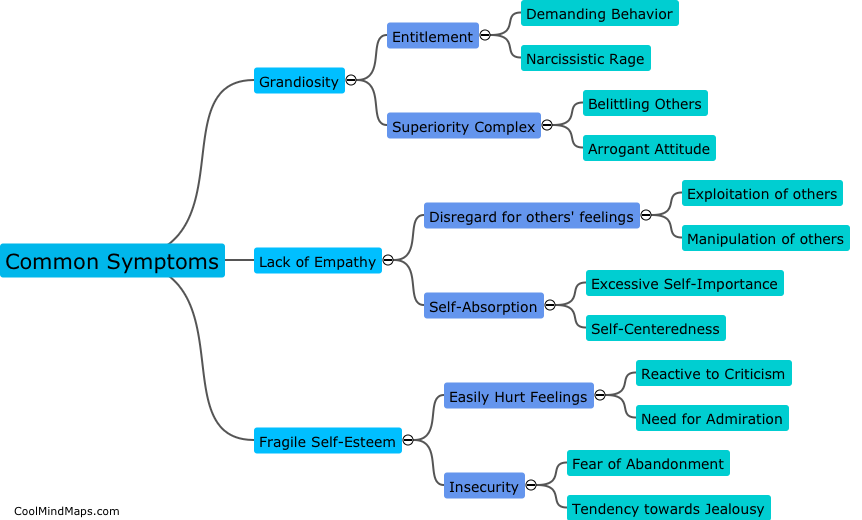
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNA molecules that play a significant role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. They are usually about 21-25 nucleotides in length and are found in plants, animals, and some viruses. miRNAs work by binding to the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules, which are responsible for carrying the genetic instructions from genes to produce proteins. By doing so, miRNAs are able to inhibit the translation process or facilitate the degradation of the mRNA, effectively silencing the target gene. This mechanism allows miRNAs to have a wide range of biological functions, including regulation of developmental processes, cell differentiation, immune response, and the onset of various diseases. The discovery of miRNAs has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation and has opened new avenues for therapeutic interventions.

This mind map was published on 5 February 2024 and has been viewed 110 times.